Deletion of the Ttf1 gene in differentiated neurons disrupts female reproduction without impairing basal ganglia function
- PMID: 17182767
- PMCID: PMC6675010
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4238-06.2006
Deletion of the Ttf1 gene in differentiated neurons disrupts female reproduction without impairing basal ganglia function
Abstract
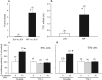
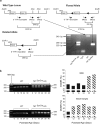
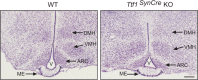
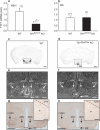
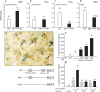
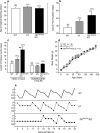
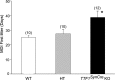
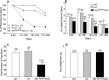
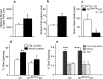
Thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF1) [also known as Nkx2.1 (related to the NK-2 class of homeobox genes) and T/ebp (thyroid-specific enhancer-binding protein)], a homeodomain gene required for basal forebrain morphogenesis, remains expressed in the hypothalamus after birth, suggesting a role in neuroendocrine function. Here, we show an involvement of TTF1 in the control of mammalian puberty and adult reproductive function. Gene expression profiling of the nonhuman primate hypothalamus revealed that TTF1 expression increases at puberty. Mice in which the Ttf1 gene was ablated from differentiated neurons grew normally and had normal basal ganglia/hypothalamic morphology but exhibited delayed puberty, reduced reproductive capacity, and a short reproductive span. These defects were associated with reduced hypothalamic expression of genes required for sexual development and deregulation of a gene involved in restraining puberty. No extrapyramidal impairments associated with basal ganglia dysfunction were apparent. Thus, although TTF1 appears to fulfill only a morphogenic function in the ventral telencephalon, once this function is satisfied in the hypothalamus, TTF1 remains active as part of the transcriptional machinery controlling female sexual development.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez-Bolado G, Rosenfeld MG, Swanson LW. Model of forebrain regionalization based on spatiotemporal patterns of POU-III homeobox gene expression, birthdates, and morphological features. J Comp Neurol. 1995;355:237–295. - PubMed
-
- Basso K, Margolin AA, Stolovitzky G, Klein U, Dalla-Favera R, Califano A. Reverse engineering of regulatory networks in human B cells. Nat Genet. 2005;37:382–390. - PubMed
-
- Bohinksi RJ, Di Lauro R, Whitsett JA. The lung-specific surfactant protein B gene promoter is a target for thyroid transcription factor 1 and hepatocyte nuclear factor 3, indicating common factors for organ-specific gene expression along the foregut axis. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:5671–5681. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davidson EH, Rast JP, Oliveri P, Ransick A, Calestani C, Yuh CH, Minokawa T, Amore G, Hinman V, Arenas-Mena C, Otim O, Brown CT, Livi CB, Lee PY, Revilla R, Rust AG, Pan Z, Schilstra MJ, Clarke PJ, Arnone MI, et al. A genomic regulatory network for development. Science. 2002;295:1669–1678. - PubMed
-
- Davis AM, Seney ML, Stallings NR, Zhao L, Parker KL, Tobet SA. Loss of steroidogenic factor 1 alters cellular topography in the mouse ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus. J Neurobiol. 2004;60:424–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
