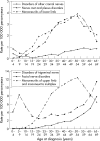
Familial risks for nerve, nerve root and plexus disorders in siblings based on hospitalisations in Sweden
- PMID: 17183020
- PMCID: PMC2465591
- DOI: 10.1136/jech.2006.046615
Familial risks for nerve, nerve root and plexus disorders in siblings based on hospitalisations in Sweden
Abstract
Background: Nerve, nerve root and plexus disorders are common diseases, but little is known about familial clustering in these diseases. This is, to our knowledge, the first systematic family study carried out on these diseases.
Methods: Familial risks for siblings who were hospitalised for nerve, nerve root and plexus disorders in Sweden were defined. A nationwide database for neurological diseases was constructed by linking the Multigeneration Register on 0-69-year-old siblings to the Hospital Discharge Register covering the years 1987-2001. Standardised risk ratios (SIRs) were calculated for affected sibling pairs by comparing them with those whose siblings had no neurological disease.
Results: 29,686 patients, 43% men and 57% women, were diagnosed at a mean age of 37.5 years. 191 siblings were hospitalised for these disorders, giving an overall SIR of 2.59 (95% CI 1.58 to 4.22), with no sex difference. Plantar nerve mononeuritis and carpal tunnel syndrome showed the highest familial risks: 4.82 (1.08 to 16.04) and 4.08 (2.07 to 7.84), respectively. Lateral poplitean and plantar nerve neuritis preferentially affected women, with SIRs of >8; disorders of the other cranial nerves affected only men, with an SIR of >10. Concordant trigeminal neuralgia, Bell's palsy and carpal tunnel syndrome showed familial risks, but, with the exception of Bell's palsy, they also showed correlation between spouses, implying environmental sharing of risk factors.
Conclusions: The results cannot distinguish between inheritable or shared environmental factors, or their interactions, but they clearly show familial clustering, suggestive of multifactorial aetiology and inviting for aetiological research.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Familial risks for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among siblings based on hospitalisations in Sweden.J Epidemiol Community Health. 2008 May;62(5):398-401. doi: 10.1136/jech.2007.063156. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2008. PMID: 18413451
-
Familial risks for asthma among twins and other siblings based on hospitalizations in Sweden.Clin Exp Allergy. 2007 Sep;37(9):1320-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2007.02737.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007. PMID: 17845412
-
Familial risks for main neurological diseases in siblings based on hospitalizations in Sweden.Twin Res Hum Genet. 2006 Aug;9(4):580-6. doi: 10.1375/183242706778024991. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 16899166
-
Familial risks for depression among siblings based on hospitalizations in Sweden.Psychiatr Genet. 2008 Apr;18(2):80-4. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0b013e3282f08ac9. Psychiatr Genet. 2008. PMID: 18349699
-
Familial risks for common diseases: etiologic clues and guidance to gene identification.Mutat Res. 2008 Mar-Apr;658(3):247-58. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2008.01.002. Epub 2008 Jan 12. Mutat Res. 2008. PMID: 18282736 Review.
Cited by
-
Neighborhood deprivation and warfarin, aspirin and statin prescription - A cohort study of men and women treated for atrial fibrillation in Swedish primary care.Int J Cardiol. 2015;187:547-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.04.005. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Int J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25863300 Free PMC article.
-
Differences and time trends in drug treatment of atrial fibrillation in men and women and doctors' adherence to warfarin therapy recommendations: a Swedish study of prescribed drugs in primary care in 2002 and 2007.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;69(2):245-53. doi: 10.1007/s00228-012-1322-6. Epub 2012 Jun 10. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22684091
-
Familial occipital neuralgia with sporadic NIN: a reply.J Headache Pain. 2011 Dec;12(6):659. doi: 10.1007/s10194-011-0383-8. Epub 2011 Sep 4. J Headache Pain. 2011. PMID: 21892799 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Preliminary Study of the Efficacy of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Trigeminal Neuralgia.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Mar 4;16:848347. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.848347. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35308616 Free PMC article.
-
Structural validity of the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire and its short version, the 6-Item CTS symptoms scale: a Rasch analysis one year after surgery.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Sep 12;21(1):609. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03626-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32919457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ropper A, Brown R.Adams and Victor's principles of neurology. 8th edn. New York: McGraw‐Hill, 2005
-
- Hentschel K, Capobianco D J, Dodick D W. Facial pain. Neurologist 200511244–249. - PubMed
-
- Gilden D. Bell's palsy. N Engl J Med 20043511323–1331. - PubMed
-
- Rempel D M, Diao E. Entrapment neuropathies: pathophysiology and pathogenesis. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 20041471–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical