Clues to neuro-degeneration in Niemann-Pick type C disease from global gene expression profiling
- PMID: 17183645
- PMCID: PMC1762405
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000019
Clues to neuro-degeneration in Niemann-Pick type C disease from global gene expression profiling
Abstract
Background: Niemann-Pick Type C (NPC) disease is a neurodegenerative disease that is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol and glycosphingolipids in the late endocytic pathway. The majority of NPC cases are due to mutations in the NPC1 gene. The precise function of this gene is not yet known.
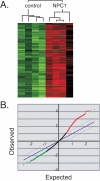
Methodology/principal findings: Using cDNA microarrays, we analyzed the genome-wide expression patterns of human fibroblasts homozygous for the I1061T NPC1 mutation that is characterized by a severe defect in the intracellular processing of low density lipoprotein-derived cholesterol. A distinct gene expression profile was identified in NPC fibroblasts from different individuals when compared with fibroblasts isolated from normal subjects. As expected, NPC1 mutant cells displayed an inappropriate homeostatic response to accumulated intracellular cholesterol. In addition, a number of striking parallels were observed between NPC disease and Alzheimer's disease.
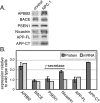
Conclusions/significance: Many genes involved in the trafficking and processing of amyloid precursor protein and the microtubule binding protein, tau, were more highly expressed. Numerous genes important for membrane traffic and the cellular regulation of calcium, metals and other ions were upregulated. Finally, NPC fibroblasts exhibited a gene expression profile indicative of oxidative stress. These changes are likely contributors to the pathophysiology of Niemann-Pick Type C disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Vanier MT, Millat G. Niemann-Pick disease type C. Clin. Genet. 2003;64:269–281. - PubMed
-
- Sturley SL, Patterson MC, Balch W, Liscum L. The pathophysiology and mechanisms of NP-C disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1685:83–87. - PubMed
-
- Carstea ED, Morris JA, Coleman KG, Loftus SK, Zhang D, et al. Niemann-Pick C1 disease gene: homology to mediators of cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1997;277:228–231. - PubMed
-
- Sever N, Yang T, Brown MS, Goldstein JL, DeBose-Boyd RA. Accelerated degradation of HMG CoA reductase mediated by binding of insig-1 to its sterol-sensing domain. Mol Cell. 2003;11:25–33. - PubMed
-
- Hua X, Nohturfft A, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Sterol resistance in CHO cells traced to point mutation in SREBP cleavage-activating protein. Cell. 1996;87:415–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

