Polymorphism in the MHC2TA gene is associated with features of the metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular mortality
- PMID: 17183695
- PMCID: PMC1762368
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000064
Polymorphism in the MHC2TA gene is associated with features of the metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular mortality
Abstract
Background: Recently, a -168A-->G polymorphism in the MHC class II transactivator gene (MHC2TA) was shown to be associated with increased susceptibility to myocardial infarction (MI).
Aim: To confirm the association between the MHC2TA -168A-->G polymorphism and MI and to study its putative role for microalbuminuria, the metabolic syndrome (MetS) and cardiovascular mortality.
Materials and methods: Using an allelic discrimination method we genotyped 11,064 individuals from three study populations: 1) 4,432 individuals from the Botnia type 2 diabetes (T2D) study, 2) 1,222 patients with MI and 2,345 control subjects participating in the Malmö Diet and Cancer study and comprising an MI case-control sample, and 3) 3,065 T2D patients from the Local Swedish Diabetes registry.
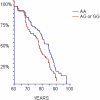
Results: No association between the -168A-->G polymorphism in MHC2TA and MI was observed. However, in the Botnia cohort the AG/GG genotypes were associated with cardiovascular mortality after MI (1.78 [1.09-2.92], p = 0.02). In addition, the AG/GG genotypes were more common in subjects with MetS (40.1% vs. 36.9%, p = 0.03) and in non-diabetic subjects with microalbuminuria (45.4% vs. 36.5%, p = 0.003) compared to control subjects.
Conclusions: A polymorphism in MHC2TA was associated with cardiovascular mortality and predictors of cardiovascular mortality, microalbuminuria and MetS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Greenland P, Knoll MD, Stamler J, Neaton JD, Dyer AR, et al. Major risk factors as antecedents of fatal and nonfatal coronary heart disease events. Jama. 2003;290:891–897. - PubMed
-
- Khot UN, Khot MB, Bajzer CT, Sapp SK, Ohman EM, et al. Prevalence of conventional risk factors in patients with coronary heart disease. Jama. 2003;290:898–904. - PubMed
-
- Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Rosner B, Speizer FE, et al. A prospective study of parental history of myocardial infarction and coronary heart disease in women. Am J Epidemiol. 1986;123:48–58. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki K, Ohnishi Y, Iida A, Sekine A, Yamada R, et al. Functional SNPs in the lymphotoxin-alpha gene that are associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction. Nat Genet. 2002;32:650–654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials