A single basis for developmental buffering of Drosophila wing shape
- PMID: 17183701
- PMCID: PMC1762351
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000007
A single basis for developmental buffering of Drosophila wing shape
Abstract
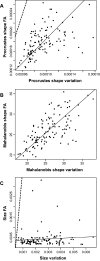
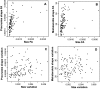
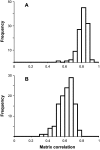
The nature of developmental buffering processes has been debated extensively, based on both theoretical reasoning and empirical studies. In particular, controversy has focused on the question of whether distinct processes are responsible for canalization, the buffering against environmental or genetic variation, and for developmental stability, the buffering against random variation intrinsic in developmental processes. Here, we address this question for the size and shape of Drosophila melanogaster wings in an experimental design with extensively replicated and fully controlled genotypes. The amounts of variation among individuals and of fluctuating asymmetry differ markedly among genotypes, demonstrating a clear genetic basis for size and shape variability. For wing shape, there is a high correlation between the amounts of variation among individuals and fluctuating asymmetry, which indicates a correspondence between the two types of buffering. Likewise, the multivariate patterns of shape variation among individuals and of fluctuating asymmetry show a close association. For wing size, however, the amounts of individual variation and fluctuating asymmetry are not correlated. There was a significant link between the amounts of variation between wing size and shape, more so for fluctuating asymmetry than for variation among individuals. Overall, these experiments indicate a considerable degree of shared control of individual variation and fluctuating asymmetry, although it appears to differ between traits.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gibson G, Dworkin IM. Uncovering cryptic genetic variation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:681–690. - PubMed
-
- Debat V, David P. Mapping phenotypes: canalization, plasticity and developmental stability. Trends Ecol Evol. 2001;16:555–561.
-
- Klingenberg CP. A developmental perspective on developmental instability: theory, models and mechanisms. In: Polak M, editor. Developmental instability: causes and consequences. New York: Oxford University Press; 2003. pp. 14–34.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

