Breastfeeding duration in mothers who express breast milk: a cohort study
- PMID: 17184553
- PMCID: PMC1764725
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-4358-1-28
Breastfeeding duration in mothers who express breast milk: a cohort study
Abstract
Background: The expression of breast milk allows a mother to be away intermittently from her infant while continuing to breastfeed. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between expression of breast milk and breastfeeding duration
Methods: A cohort study of 12 months duration. The mothers were recruited from two public maternity hospitals in Perth, Australia between mid-September 2002 and mid-July 2003. While in hospital, participating mothers completed a questionnaire that included questions on how they were feeding their newborn. Telephone interviews conducted at regular periods monitored changes in infant feeding practices, including expression of breast milk. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was used to explore the association between breast milk expression and the duration of any breastfeeding.
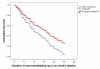
Results: A total of 587 mothers, or 55% of those eligible, participated in the study. Of these 93.5% were breastfeeding at discharge from hospital. Mothers who expressed breast milk (at one or more time periods) were less likely to discontinue any breastfeeding before six months (Relative Risk 0.71, 95% CI 0.52, 0.98) than those who had never expressed milk.
Conclusion: This study found that mothers who express breast milk are more likely to breastfeed to six months (any breastfeeding). While further research is required in different cultures to confirm these results, the appropriate use of expressed breast milk may be a means to help mothers to achieve six months of full breastfeeding while giving more lifestyle options.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the impact of breast milk expression in early postpartum period on breastfeeding duration: a prospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2015 Oct 20;15:268. doi: 10.1186/s12884-015-0698-6. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2015. PMID: 26487378 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of breastfeeding support provided by trained clinicians during an early, routine, preventive visit: a prospective, randomized, open trial of 226 mother-infant pairs.Pediatrics. 2005 Feb;115(2):e139-46. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1362. Pediatrics. 2005. PMID: 15687421 Clinical Trial.
-
National targets for breastfeeding at hospital discharge have been achieved in Perth.Acta Paediatr. 2005 Mar;94(3):352-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2005.tb03079.x. Acta Paediatr. 2005. PMID: 16028655
-
Nutrition, growth, and allergic diseases among very preterm infants after hospital discharge.Dan Med J. 2013 Feb;60(2):B4588. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23461996 Review.
-
Role of breast-feeding in the prevention and treatment of diarrhoea.J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1990 Sep;8(3):68-81. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1990. PMID: 2243179 Review.
Cited by
-
Breast milk expression among formally employed women in urban and rural Malaysia: A qualitative study.Int Breastfeed J. 2012 Aug 29;7(1):11. doi: 10.1186/1746-4358-7-11. Int Breastfeed J. 2012. PMID: 22929649 Free PMC article.
-
A study on parental awareness of feeding practices in children in the age-group 12-24 months.J Prev Med Hyg. 2022 Jan 31;62(4):E909-E917. doi: 10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.4.2287. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Prev Med Hyg. 2022. PMID: 35603241 Free PMC article.
-
Commercialisation and commodification of breastfeeding: video diaries by first-time mothers.Int Breastfeed J. 2020 May 1;15(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13006-020-00264-1. Int Breastfeed J. 2020. PMID: 32354372 Free PMC article.
-
A cohort study of infant feeding practices in city, suburban and rural areas in Zhejiang Province, PR China.Int Breastfeed J. 2008 Mar 3;3:4. doi: 10.1186/1746-4358-3-4. Int Breastfeed J. 2008. PMID: 18315865 Free PMC article.
-
The quiet revolution: breastfeeding transformed with the use of breast pumps.Am J Public Health. 2011 Aug;101(8):1356-9. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2011.300136. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Am J Public Health. 2011. PMID: 21680919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Graham KI, Scott JA, Binns CW, Oddy WH. National targets for breastfeeding at hospital discharge have been achieved in Perth. Acta Paediatr. 2005;94:352–356. - PubMed
-
- Australian Bureau of Statistics . Australian Social Trends 2001. Catalogue no. 4102.0. Canberra , Australian Bureau of Statistics; 2004.
-
- Human Rights and Equal Opportunity Commission . Valuing Parenthood: Options for Paid Maternity Leave. Sydney , HREOC; 2002.
-
- O'Neill S. Paid Maternity Leave: E-Brief . Parliament of Australia; 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources