Amblyopia in astigmatic children: patterns of deficits
- PMID: 17184807
- PMCID: PMC1861829
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2006.11.008
Amblyopia in astigmatic children: patterns of deficits
Abstract
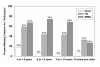
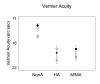
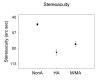
Neural changes that result from disruption of normal visual experience during development are termed amblyopia. To characterize visual deficits specific to astigmatism-related amblyopia, we compared best-corrected visual performance in 330 astigmatic and 475 non-astigmatic kindergarten through 6th grade children. Astigmatism was associated with deficits in letter, grating and vernier acuity, high and middle spatial frequency contrast sensitivity, and stereoacuity. Although grating acuity, vernier acuity, and contrast sensitivity were reduced across stimulus orientation, astigmats demonstrated orientation-dependent deficits (meridional amblyopia) only for grating acuity. Astigmatic children are at risk for deficits across a range of visual functions.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Development and treatment of astigmatism-related amblyopia.Optom Vis Sci. 2009 Jun;86(6):634-9. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e3181a6165f. Optom Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19430327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amblyopia in astigmatic preschool children.Vision Res. 2003 Apr;43(9):1081-90. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6989(03)00014-2. Vision Res. 2003. PMID: 12676249
-
Changes in visual function following optical treatment of astigmatism-related amblyopia.Vision Res. 2008 Mar;48(6):773-87. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2007.12.007. Epub 2008 Feb 7. Vision Res. 2008. PMID: 18261760 Free PMC article.
-
Amblyopia in astigmatic infants and toddlers.Optom Vis Sci. 2010 May;87(5):330-6. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e3181d951c8. Optom Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20351602 Free PMC article.
-
From visual acuity to hyperacuity: a 10-year update.Can J Psychol. 1989 Jun;43(2):109-20. doi: 10.1037/h0084217. Can J Psychol. 1989. PMID: 2486491 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations between anisometropia, amblyopia, and reduced stereoacuity in a school-aged population with a high prevalence of astigmatism.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Oct;49(10):4427-36. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-1985. Epub 2008 Jun 6. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18539935 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring Retinal Thickness and Visual Acuity in Eyes with Different Types of Astigmatism in a Cohort of Hong Kong Chinese Adults.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Jan 3;64(1):2. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.1.2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 36595274 Free PMC article.
-
Higher-order aberrations and best-corrected visual acuity in Native American children with a high prevalence of astigmatism.J AAPOS. 2015 Aug;19(4):352-7.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J AAPOS. 2015. PMID: 26239206 Free PMC article.
-
Children's Ocular Components and Age, Gender, and Ethnicity.Optom Vis Sci. 2009 Aug;86(8):918-35. doi: 10.1097/opx.0b013e3181b2f903. Optom Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19650241 Free PMC article.
-
Normative monocular visual acuity for early treatment diabetic retinopathy study charts in emmetropic children 5 to 12 years of age.Ophthalmology. 2009 Jul;116(7):1397-401. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.01.019. Epub 2009 May 8. Ophthalmology. 2009. PMID: 19427702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appelle S. Perception and discrimination as a function of stimulus orientation: the “oblique effect” in man and animals. Psychological Bulletin. 1972;78:266–278. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson J, Braddick O, Bobier B, Anker S, Ehrlich D, King J, Watson P, Moore A. Two infant vision screening programmes: prediction and prevention of strabismus and amblyopia from photo- and videorefractive screening. Eye. 1996;10:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Birch E, Williams C, Hunter J, Lapa MC, the ALSPAC “Children in Focus” Study Team Random dot stereoacuity of preschool children. Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology & Strabismus. 1997;34:217–222. - PubMed
-
- Boothe RG, Teller DY. Meridional variations in acuity and CSF's in monkeys (Macaca nemestrina) reared with externally applied astigmatism. Vision Research. 1982;22:801–810. - PubMed
-
- Chen SI, Hove M, McCloskey CL, Kaye SB. The effect of monocularly and binocularly induced astigmatic blur on depth discrimination is orientation dependent. Optometry and Vision Science. 2005;82:101–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

