The case for 8,5'-cyclopurine-2'-deoxynucleosides as endogenous DNA lesions that cause neurodegeneration in xeroderma pigmentosum
- PMID: 17184928
- PMCID: PMC2430073
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.10.025
The case for 8,5'-cyclopurine-2'-deoxynucleosides as endogenous DNA lesions that cause neurodegeneration in xeroderma pigmentosum
Abstract
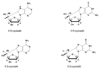
Patients with the genetic disease xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) lack the capacity to carry out a specific type of DNA repair process called nucleotide excision repair (NER). The NER pathway plays a critical role in the repair of DNA damage resulting from ultraviolet (UV) radiation. A subset of XP patients develops a profound neurodegenerative condition known as XP neurological disease. Robbins and colleagues [Andrews A, Barrett S, Robbins J (1978) Xeroderma pigmentosum neurological abnormalities correlate with the colony forming ability after ultraviolet irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 75:1984-1988] hypothesized that since UV light cannot reach into the human brain, XP neurological disease results from some form of endogenous DNA damage that is normally repaired by the NER pathway. In the absence of NER, the damage accumulates, causing neuronal death by blocking transcription. In this manuscript, I consider the evidence that a particular class of oxidative DNA lesions, the 8,5'-cyclopurine-2'-deoxynucleosides, fulfills many of the criteria expected of neurodegenerative DNA lesions in XP. Specifically, these lesions are chemically stable, endogenous DNA lesions that are repaired by the NER pathway but not by any other known process, and strongly block transcription by RNA polymerase II in cells from XP patients. A similar set of criteria might be used to evaluate other candidate DNA lesions responsible for neurological diseases resulting from defects in other DNA repair mechanisms as well.
Figures


References
-
- Brooks PJ, Wise DS, Berry DA, Kosmoski JV, Smerdon MJ, Somers RL, Mackie H, Spoonde AY, Ackerman EJ, Coleman K, Tarone RE, Robbins JH. The oxidative DNA lesion 8,5'-(S)-cyclo-2'-deoxyadenosine is repaired by the nucleotide excision repair pathway and blocks gene expression in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:22355–22362. - PubMed
-
- Brumback RA, Brooks PJ, Leech R. Cockayne Syndrome. In: Golden J, Harding B, editors. Pediatric Neuropathology. Pegnitz: International Society of Neuropathology Press; 2004.
-
- Burcham PC. Genotoxic lipid peroxidation products: their DNA damaging properties and role in formation of endogenous DNA adducts. Mutagenesis. 1998;13:287–305. - PubMed
-
- Cadenas E, Davies KJ. Mitochondrial free radical generation, oxidative stress, and aging. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;29:222–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

