Transient regulatory T-cells: a state attained by all activated human T-cells
- PMID: 17185041
- PMCID: PMC1868523
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.10.014
Transient regulatory T-cells: a state attained by all activated human T-cells
Abstract
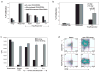
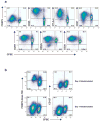
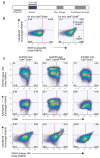
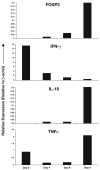
CD4(+)CD25(+)FOXP3(+) regulatory T-cells (T(regs)) form an important arm of the immune system responsible for suppressing untoward immune responses. T(regs) can be thymically derived or peripherally induced, even from CD4(+)CD25(-)FOXP3(-) T-cells. FOXP3 expression and in vitro suppressive activity are considered unique hallmarks of this dedicated and stable lineage of regulatory cells. Here we show that virtually all human CD4(+)CD25(-)FOXP3(-) T-cells and CD8(+)CD25(-)FOXP3(-) T-cells attain a transient FOXP3(+)CD25(+) state during activation. In this state of activation, these cells possess the classic phenotype of T(regs), in that they express similar markers and inhibit in vitro proliferation of autologous CD4(+)CD25(-) T-cells. This state is characterized by suppressed IFN-gamma production and robust TNF-alpha and IL-10 production. Interestingly, the great majority of the activated cells eventually downregulate FOXP3 expression, with a concomitant drop in suppressive ability. Our results show that, in humans, FOXP3 expression and T(reg) functionality are not exclusive features of a stable or unique lineage of T-cells but may also be a transient state attained by almost all T-cells. These results warrant caution in interpreting human studies using FOXP3 and suppressive activity as readouts and suggest that attempts to induce "T(regs)" may paradoxically result in induction of effector T-cells, unless stability is confirmed.
Figures

References
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:345–52. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:330–6. - PubMed
-
- Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003;299:1057–61. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Williams LM, Dooley JL, Farr AG, Rudensky AY. Regulatory T cell lineage specification by the forkhead transcription factor foxp3. Immunity. 2005;22:329–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

