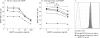Decreased B cell activating factor receptor expression on peripheral lymphocytes associated with increased disease activity in primary Sjögren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 17185325
- PMCID: PMC1954659
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.065656
Decreased B cell activating factor receptor expression on peripheral lymphocytes associated with increased disease activity in primary Sjögren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: To analyse B cell activating factor (BAFF) receptor (BAFF-R) expression on peripheral lymphocytes from patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
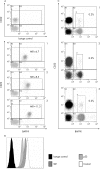
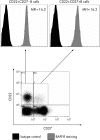
Patients and methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 20 patients with pSS, 19 patients with SLE and 15 controls were examined by flow cytometry to investigate BAFF-R mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) on lymphocytes. BAFF-R mRNA level from isolated blood B cells of nine patients with pSS and eight controls was assessed by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. BAFF serum level was determined by ELISA.
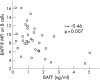
Results: In all subjects, BAFF-R was expressed on all naïve CD27- and memory CD27+ B-cells and was present on <0.5% of T cells. The expression of BAFF-R on B cells was significantly decreased in patients with pSS as compared with controls (MFI = 7.8 vs 10.6, p = 0.001), and was intermediate in patients with SLE (MFI = 9.5). Serum BAFF level was inversely correlated with BAFF-R MFI (p = 0.007), but not because of competition between endogenous BAFF (at observed concentrations in patients) and the monoclonal antibody (11C1) detecting BAFF-R. BAFF-R mRNA levels did not differ between patients with pSS and controls (p = 0.48). BAFF-R MFI decreased after overnight culture with recombinant human BAFF (from 32.5 to 25.4, p = 0.03). Contrary to the serum BAFF level, BAFF-R expression was correlated with extraglandular involvement in pSS and SLE Disease Activity Index.
Conclusions: BAFF-R expression is reduced on peripheral B cells of patients with pSS and SLE. This down-regulation occurs through a post-transcriptional mechanism and could be the consequence of chronic increase in BAFF. BAFF-R levels on B cells could be a novel activity biomarker in autoimmune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
References
-
- Martin F, Chan A C. B cell immunobiology in disease: evolving concepts from the clinic. Annu Rev Immunol 200624467–496. - PubMed
-
- Dorner T, Lipsky P E. Signalling pathways in B‐cells: implications for autoimmunity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2006305213–240. - PubMed
-
- Carter R H. B‐cells in health and disease. Mayo Clin Proc 200681377–384. - PubMed
-
- Mackay F, Schneider P, Rennert P, Browning J. BAFF AND APRIL: a tutorial on B cell survival. Annu Rev Immunol 200321231–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials