Use of hydrodissection to prevent nerve and muscular damage during radiofrequency ablation of kidney tumors
- PMID: 17185695
- PMCID: PMC2555976
- DOI: 10.1097/01.RVI.0000248829.49442.0E
Use of hydrodissection to prevent nerve and muscular damage during radiofrequency ablation of kidney tumors
Abstract
Muscular complications are uncommon but have been reported after radiofrequency (RF) ablation of renal tumors. Ablation of renal lesions near the psoas muscle may result in paresthesia in the distribution of the genitofemoral nerve. The present report describes a case of sensory and muscular dysfunction after RF ablation of a renal lesion lying on top of the psoas muscle that was treated without hydrodissection. To prevent this complication, hydrodissection was effectively used in two other patients during RF ablation of lesions abutting or in close proximity to the psoas muscle.
Figures
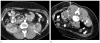
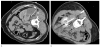
References
-
- Farrell MA, Charboneau JW, Callstrom MR, et al. Paranephric water instillation: a technique to prevent bowel injury during percutaneous renal radio frequency ablation. Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181:1315–1317. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DB, Solomon SB, Su LM, et al. Defining the complications of cryoablation and radio frequency ablation of small renal tumors: a multi-institutional review. J Urol. 2004;172:874–87. - PubMed
-
- Bhayani SB, Allaf ME, Su LM, et al. Neuromuscular complications after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of renal tumors. Urology. 2005;65:592. - PubMed
-
- Boss A, Clasen S, Kuczyk M, et al. Thermal damage of the genitofemoral nerve due to radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinoma: a potentially avoidable complication. Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185:1627–1631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

