Tricellulin is a tight-junction protein necessary for hearing
- PMID: 17186462
- PMCID: PMC1698716
- DOI: 10.1086/510022
Tricellulin is a tight-junction protein necessary for hearing
Abstract
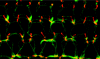
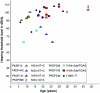
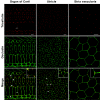
The inner ear has fluid-filled compartments of different ionic compositions, including the endolymphatic and perilymphatic spaces of the organ of Corti; the separation from one another by epithelial barriers is required for normal hearing. TRIC encodes tricellulin, a recently discovered tight-junction (TJ) protein that contributes to the structure and function of tricellular contacts of neighboring cells in many epithelial tissues. We show that, in humans, four different recessive mutations of TRIC cause nonsyndromic deafness (DFNB49), a surprisingly limited phenotype, given the widespread tissue distribution of tricellulin in epithelial cells. In the inner ear, tricellulin is concentrated at the tricellular TJs in cochlear and vestibular epithelia, including the structurally complex and extensive junctions between supporting and hair cells. We also demonstrate that there are multiple alternatively spliced isoforms of TRIC in various tissues and that mutations of TRIC associated with hearing loss remove all or most of a conserved region in the cytosolic domain that binds to the cytosolic scaffolding protein ZO-1. A wild-type isoform of tricellulin, which lacks this conserved region, is unaffected by the mutant alleles and is hypothesized to be sufficient for structural and functional integrity of epithelial barriers outside the inner ear.
Figures






References
Web Resources
-
- Apple, http://www.apple.com/quicktime/download/win.html (for QuickTime download)
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for residues 119–135 [accession number DQ682659] and 212–282 [accession number DQ682659], ZO1-N [accession number AAA02891], and exons for TRIC-a [accession number DQ682656], TRIC-a1 [accession number DQ682657], TRIC-b [accession number NM144724], TRIC-c [accession number DQ682658], Tric-a [accession number DQ682659], Tric-b [accession number DQ682660], and Tric-c [accession number DQ682661])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for DFNB29) - PubMed
-
- Pfam, http://www.sanger.ac.uk/Software/Pfam/ (for occludin-ELL [accession number PF07303])
References
-
- Sterkers O, Ferrary E, Amiel C (1988) Production of inner ear fluids. Physiol Rev 68:1083–1128 - PubMed
-
- Jahnke K (1975) The fine structure of freeze-fractured intercellular junctions in the guinea pig inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 336:1–40 - PubMed
-
- Wilcox ER, Burton QL, Naz S, Riazuddin S, Smith TN, Ploplis B, Belyantseva I, Ben-Yosef T, Liburd NA, Morell RJ, Kachar B, Wu DK, Griffith AJ, Riazuddin S, Friedman TB (2001) Mutations in the gene encoding tight junction claudin-14 cause autosomal recessive deafness DFNB29. Cell 104:165–17210.1016/S0092-8674(01)00200-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

