NTP-CERHR expert panel report on the reproductive and developmental toxicity of genistein
- PMID: 17186522
- PMCID: PMC2020434
- DOI: 10.1002/bdrb.20087
NTP-CERHR expert panel report on the reproductive and developmental toxicity of genistein
Figures
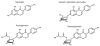
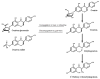



References
-
- Adachi T, Ono Y, Koh KB, Takashima K, Tainaka H, Matsuno Y, Nakagawa S, Todaka E, Sakurai K, Fukata H, Iguchi T, Komiyama M, Mori C. Long-term alteration of gene expression without morphological change in testis after neonatal exposure to genistein in mice: toxicogenomic analysis using cDNA microarray. Food Chem Toxicol. 2004;42:445–452. - PubMed
-
- Adeoya-Osiguwa SA, Markoulaki S, Pocock V, Milligan SR, Fraser LR. 17beta-Estradiol and environmental estrogens significantly affect mammalian sperm function. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:100–107. - PubMed
-
- Adlercreutz H. Phytooestrogens and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3:364–373. - PubMed
-
- Adlercreutz H, Fotsis T, Lampe J, Wahala K, Makela T, Brunow G, Hase T. Quantitative determination of lignans and isoflavonoids in plasma of omnivorous and vegetarian women by isotope dilution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1993a;215:5–18. - PubMed
-
- Adlercreutz H, Markkanen H, Watanabe S. Plasma Concentrations of PhytoOestrogens in Japanese Men. Lancet. 1993b;342:1209–1210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

