DNA translocation and loop formation mechanism of chromatin remodeling by SWI/SNF and RSC
- PMID: 17188033
- PMCID: PMC9034902
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.10.025
DNA translocation and loop formation mechanism of chromatin remodeling by SWI/SNF and RSC
Abstract
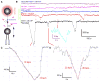
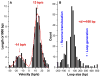
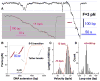
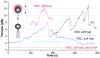
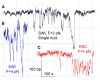
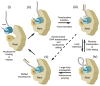
ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes (remodelers) modulate gene transcription by regulating the accessibility of highly packaged genomic DNA. However, the molecular mechanisms involved at the nucleosomal level in this process remain controversial. Here, we monitor the real-time activity of single ySWI/SNF or RSC complexes on single, stretched nucleosomal templates under tensions above 1 pN forces. We find that these remodelers can translocate along DNA at rates of approximately 13 bp/s and generate forces up to approximately 12 pN, producing DNA loops of a broad range of sizes (20-1200 bp, average approximately 100 bp) in a nucleosome-dependent manner. This nucleosome-specific activity differs significantly from that on bare DNA observed under low tensions and suggests a nucleosome-remodeling mechanism through intranucleosomal DNA loop formation. Such loop formation may provide a molecular basis for the biological functions of remodelers.
Figures
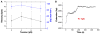
Similar articles
-
Architecture of the chromatin remodeler RSC and insights into its nucleosome engagement.Elife. 2019 Dec 30;8:e54449. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54449. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31886770 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin remodeling by ISW2 and SWI/SNF requires DNA translocation inside the nucleosome.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006 Apr;13(4):339-46. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1071. Epub 2006 Mar 5. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16518397
-
The core histone N-terminal domains are required for multiple rounds of catalytic chromatin remodeling by the SWI/SNF and RSC complexes.Biochemistry. 1999 Feb 23;38(8):2514-22. doi: 10.1021/bi982109d. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10029546
-
Chromatin remodeling: insights and intrigue from single-molecule studies.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Nov;14(11):989-96. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1333. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17984961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin-remodeling and the initiation of transcription.Q Rev Biophys. 2015 Nov;48(4):465-70. doi: 10.1017/S0033583515000116. Q Rev Biophys. 2015. PMID: 26537406 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription-induced DNA supercoiling: New roles of intranucleosomal DNA loops in DNA repair and transcription.Transcription. 2016 May 26;7(3):91-5. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2016.1182240. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Transcription. 2016. PMID: 27115204 Free PMC article.
-
Human ISWI chromatin-remodeling complexes sample nucleosomes via transient binding reactions and become immobilized at active sites.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 16;107(46):19873-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003438107. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20974961 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin remodelers couple inchworm motion with twist-defect formation to slide nucleosomal DNA.PLoS Comput Biol. 2018 Nov 5;14(11):e1006512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006512. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 30395604 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the chromatin remodelling enzyme Chd1 bound to a ubiquitinylated nucleosome.Elife. 2018 Aug 6;7:e35720. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35720. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30079888 Free PMC article.
-
Extra views on structure and dynamics of DNA loops on nucleosomes studied with molecular simulations.Nucleus. 2016 Nov;7(6):554-559. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2016.1260800. Nucleus. 2016. PMID: 27874316 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amitani I, Baskin RJ, Kowalczykowski SC. Visualization of Rad54, a chromatin remodeling protein, translocating on single DNA molecules. Mol Cell. 2006;23:143–148. - PubMed
-
- Bochar DA, Wang L, Beniya H, Kinev A, Xue YT, Lane WS, Wang WD, Kashanchi F, Shiekhattar R. BRCA1 is associated with a human SWI/SNF-related complex: linking chromatin remodeling to breast cancer. Cell. 2000;102:257–265. - PubMed
-
- Brower-Toland B, Wacker DA, Fulbright RM, Lis JT, Kraus WL, Wang MD. Specific contributions of histone tails and their acetylation to the mechanical stability of nucleosomes. J Mol Biol. 2005;346:135–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

