G protein coupled receptor structure and activation
- PMID: 17188232
- PMCID: PMC1876727
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.10.021
G protein coupled receptor structure and activation
Abstract
G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) are remarkably versatile signaling molecules. The members of this large family of membrane proteins are activated by a spectrum of structurally diverse ligands, and have been shown to modulate the activity of different signaling pathways in a ligand specific manner. In this manuscript I will review what is known about the structure and mechanism of activation of GPCRs focusing primarily on two model systems, rhodopsin and the beta(2) adrenoceptor.
Figures
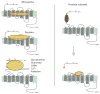


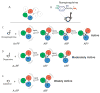

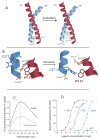
References
-
- Ballesteros JA, Weinstein H. Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G protein coupled receptors. Meth Neurosci. 1995;25:366–428.
-
- Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK. Transduction of receptor signals by beta-arrestins. Science. 2005;308(5721):512–7. - PubMed
-
- Luttrell LM, Lefkowitz RJ. The role of beta-arrestins in the termination and transduction of G-protein-coupled receptor signals. J Cell Sci. 2002;115(Pt 3):455–65. - PubMed
-
- Fredriksson R, Lagerstrom MC, Lundin LG, Schioth HB. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;63(6):1256–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

