Interleukin-10 is not a critical regulator of infarct healing and left ventricular remodeling
- PMID: 17188669
- PMCID: PMC1924681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.11.028
Interleukin-10 is not a critical regulator of infarct healing and left ventricular remodeling
Abstract
Objective: Interleukin-10 (IL-10) exerts potent anti-inflammatory actions and modulates matrix metalloproteinase expression. We hypothesized that endogenous IL-10 may regulate infarct healing and left ventricular remodeling by promoting resolution of the post-infarction inflammatory response and by modulating extracellular matrix metabolism.
Methods: IL-10 null and wildtype (WT) mice underwent reperfused infarction protocols. We compared the healing response and remodeling-associated parameters between IL-10-/-and WT infarcts. In addition, we studied the effects of IL-10 on inflammatory gene synthesis by stimulated murine cardiac fibroblasts.
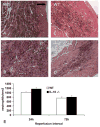
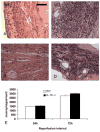
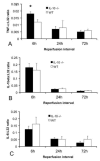
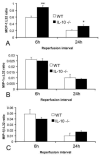
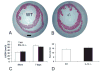
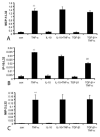
Results: Infarcted IL-10-/-mice exhibited comparable mortality rates with WT animals. Although IL-10-/-mice had higher peak tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1/CCL2 mRNA levels in the infarcted heart than WT mice, both groups demonstrated timely repression of pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine mRNA synthesis after 24 h of reperfusion and exhibited a similar time course of resolution of the neutrophil infiltrate. IL-10 gene disruption did not alter fibrous tissue deposition and dilative remodeling of the infarcted heart. Pre-incubation with IL-10 did not modulate the pro-inflammatory phenotype of TNF-alpha-stimulated cardiac fibroblasts, failing to inhibit chemokine mRNA synthesis. In contrast, transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 pre-incubation suppressed interferon-gamma-inducible protein (IP)-10/CXCL10 synthesis by cardiac fibroblasts exposed to TNF-alpha.
Conclusions: IL-10 signaling plays a non-critical role in suppression of inflammatory mediators, resolution of the inflammatory response, and fibrous tissue deposition following myocardial infarction. This may be due to the relative selectivity of IL-10-mediated anti-inflammatory actions, with respect to cell type and stimulus. Resolution of post-infarction inflammation is likely to involve multiple overlapping regulatory mechanisms controlling various pro-inflammatory pathways activated in the infarcted myocardium.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD44 is critically involved in infarct healing by regulating the inflammatory and fibrotic response.J Immunol. 2008 Feb 15;180(4):2625-33. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.4.2625. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18250474
-
CCL2/Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 regulates inflammatory responses critical to healing myocardial infarcts.Circ Res. 2005 Apr 29;96(8):881-9. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000163017.13772.3a. Epub 2005 Mar 17. Circ Res. 2005. PMID: 15774854
-
IL-10 is induced in the reperfused myocardium and may modulate the reaction to injury.J Immunol. 2000 Sep 1;165(5):2798-808. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.5.2798. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10946312
-
The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Res. 2002 Jan;53(1):31-47. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(01)00434-5. Cardiovasc Res. 2002. PMID: 11744011 Review.
-
The mechanistic basis of infarct healing.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006 Nov-Dec;8(11-12):1907-39. doi: 10.1089/ars.2006.8.1907. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006. PMID: 17034340 Review.
Cited by
-
The Biological Basis for Cardiac Repair After Myocardial Infarction: From Inflammation to Fibrosis.Circ Res. 2016 Jun 24;119(1):91-112. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303577. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 27340270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the chemokines in cardiac repair.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(12):1971-9. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990449. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23844733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro/Anti-inflammatory cytokine imbalance in postischemic left ventricular remodeling.Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:974694. doi: 10.1155/2010/974694. Epub 2010 May 9. Mediators Inflamm. 2010. PMID: 20467464 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in the chronic autoimmune response to myocardial infarction.Clin Sci (Lond). 2025 Jun 17;139(12):627-48. doi: 10.1042/CS20243091. Clin Sci (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40526105 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the inflammatory response in cardiac repair.Circ Res. 2012 Jan 6;110(1):159-73. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.243162. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22223212 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nian M, Lee P, Khaper N, Liu P. Inflammatory cytokines and postmyocardial infarction remodeling. Circ Res. 2004;94:1543–53. - PubMed
-
- Frangogiannis NG. Targeting the inflammatory response in healing myocardial infarcts. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13:1877–93. - PubMed
-
- Frangogiannis NG. The mechanistic basis of infarct healing. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8:1907–39. - PubMed
-
- Crawford SE, Stellmach V, Murphy-Ullrich JE, Ribeiro SM, Lawler J, Hynes RO, et al. Thrombospondin-1 is a major activator of TGF-beta1 in vivo. Cell. 1998;93:1159–70. - PubMed
-
- Frangogiannis NG, Ren G, Dewald O, Zymek P, Haudek S, Koerting A, et al. The critical role of endogenous Thrombospondin (TSP)-1 in preventing expansion of healing myocardial infarcts. Circulation. 2005;111:2935–2942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

