Gapex-5, a Rab31 guanine nucleotide exchange factor that regulates Glut4 trafficking in adipocytes
- PMID: 17189207
- PMCID: PMC1779820
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.12.006
Gapex-5, a Rab31 guanine nucleotide exchange factor that regulates Glut4 trafficking in adipocytes
Abstract
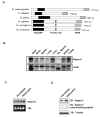
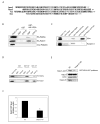
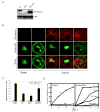
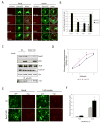
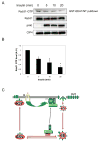
Insulin stimulates glucose uptake by promoting translocation of the Glut4 glucose transporter from intracellular storage compartments to the plasma membrane. In the absence of insulin, Glut4 is retained intracellularly; the mechanism underlying this process remains uncertain. Using the TC10-interacting protein CIP4 as bait in a yeast two-hybrid screen, we cloned a RasGAP and VPS9 domain-containing protein, Gapex-5/RME-6. The VPS9 domain is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rab31, a Rab5 subfamily GTPase implicated in trans-Golgi network (TGN)-to-endosome trafficking. Overexpression of Rab31 blocks insulin-stimulated Glut4 translocation, whereas knockdown of Rab31 potentiates insulin-stimulated Glut4 translocation and glucose uptake. Gapex-5 is predominantly cytosolic in untreated cells; its overexpression promotes intracellular retention of Glut4 in adipocytes. Insulin recruits the CIP4/Gapex-5 complex to the plasma membrane, thus reducing Rab31 activity and permitting Glut4 vesicles to translocate to the cell surface, where Glut4 docks and fuses to transport glucose into the cell.
Figures


References
-
- Ahn MY, Katsanakis KD, Bheda F, Pillay TS. Primary and essential role of the adaptor protein APS for recruitment of both c-Cbl and its associated protein CAP in insulin signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:21526–21532. - PubMed
-
- Aspenstrom P. A Cdc42 target protein with homology to the non-kinase domain of FER has a potential role in regulating the actin cytoskeleton. Curr Biol. 1997;7:479–487. - PubMed
-
- Bao X, Faris AE, Jang EK, Haslam RJ. Molecular cloning, bacterial expression and properties of Rab31 and Rab32. Eur J Biochem. 2002;269:259–271. - PubMed
-
- Baumann CA, Ribon V, Kanzaki M, Thurmond DC, Mora S, Shigematsu S, Bickel PE, Pessin JE, Saltiel AR. CAP defines a second signalling pathway required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. Nature. 2000;407:202–207. - PubMed
-
- Bogan JS, Hendon N, McKee AE, Tsao TS, Lodish HF. Functional cloning of TUG as a regulator of GLUT4 glucose transporter trafficking. Nature. 2003;425:727–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

