A family of microRNAs present in plants and animals
- PMID: 17189346
- PMCID: PMC1785418
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.044420
A family of microRNAs present in plants and animals
Abstract
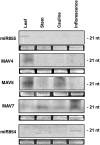
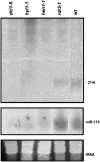
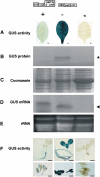
Although many miRNAs are deeply conserved within each kingdom, none are known to be conserved between plants and animals. We identified Arabidopsis thaliana miR854 and miR855, two microRNAs (miRNAs) with multiple binding sites in the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of OLIGOURIDYLATE binding PROTEIN1b (At UBP1b), forming miRNA:mRNA interactions similar to those that cause translational repression/mRNA cleavage in animals. At UBP1b encodes a member of a heterogeneous nuclear RNA binding protein (hnRNP) family. The 3'UTR of At UBP1b is sufficient to repress reporter protein expression in tissues expressing miR854 or miR855 (rosette leaves and flowers, respectively) but not where both miRNAs are absent (cauline leaves). Intergenic regions containing sequences closely resembling miR854 are predicted to fold into stable miRNA precursors in animals, and members of the miR854 family are expressed in Caenorhabditis elegans, Mus musculus, and Homo sapiens, all with imperfect binding sites in the 3'UTR of genes encoding the T cell Intracellular Antigen-Related protein, an hnRNP of the UBP1 family. Potential binding sites for miR854 are absent from UBP1-like genes in fungi lacking the miRNA biogenetic machinery. Our results indicate that plants and animals share miRNAs of the miR854 family, suggesting a common origin of these miRNAs as regulators of basal transcriptional mechanisms.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Computational analysis of microRNA targets in Caenorhabditis elegans.Gene. 2006 Jan 3;365:2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.09.035. Epub 2005 Dec 13. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16356665
-
Efficient silencing of endogenous microRNAs using artificial microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Plant. 2011 Jan;4(1):157-70. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssq061. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Mol Plant. 2011. PMID: 20943811
-
Regulation of ABCG2 expression at the 3' untranslated region of its mRNA through modulation of transcript stability and protein translation by a putative microRNA in the S1 colon cancer cell line.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;28(17):5147-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00331-08. Epub 2008 Jun 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18573883 Free PMC article.
-
Small but influential: the role of microRNAs on gene regulatory network and 3'UTR evolution.J Genet Genomics. 2009 Jan;36(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(09)60001-1. J Genet Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19161940 Review.
-
Transposable element small RNAs as regulators of gene expression.Trends Genet. 2012 Dec;28(12):616-23. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2012.09.001. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Trends Genet. 2012. PMID: 23040327 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of microRNAs in plant drought tolerance.Plant Biotechnol J. 2015 Apr;13(3):293-305. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12318. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Plant Biotechnol J. 2015. PMID: 25583362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The small RNA repertoire of Dictyostelium discoideum and its regulation by components of the RNAi pathway.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(20):6714-26. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm707. Epub 2007 Oct 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17916577 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation and divergence of microRNAs and their functions in Euphorbiaceous plants.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(3):981-95. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1035. Epub 2009 Nov 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19942686 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and functional diversification of MIRNA genes.Plant Cell. 2011 Feb;23(2):431-42. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.082784. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21317375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Lin28 homologue reprograms differentiated cells to stem cells in the moss Physcomitrella patens.Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 27;8:14242. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14242. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28128346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, E., Xie, Z., Gustafson, A.M., and Carrington, J.C. (2005). MicroRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 121 207–221. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Ambros, V. (2003). MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: Growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 113 673–676. - PubMed
-
- Ambros, V. (2004). The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431 350–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

