The role of the basal ganglia and cerebellum in language processing
- PMID: 17189619
- PMCID: PMC2424405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.11.074
The role of the basal ganglia and cerebellum in language processing
Abstract
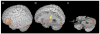
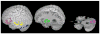
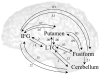
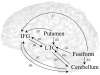
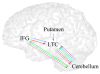
The roles of the cerebellum and basal ganglia have typically been confined in the literature to motor planning and control. However, mounting evidence suggests that these structures are involved in more cognitive domains such as language processing. In the current study, we looked at effective connectivity (the influence that one brain region has on another) of the cerebellum and basal ganglia with regions thought to be involved in phonological processing, i.e. left inferior frontal gyrus and left lateral temporal cortex. We analyzed functional magnetic resonance imaging data (fMRI) obtained during a rhyming judgment task in adults using dynamic causal modeling (DCM). The results showed that the cerebellum has reciprocal connections with both left inferior frontal gyrus and left lateral temporal cortex, whereas the putamen has unidirectional connections into these two brain regions. Furthermore, the connections between cerebellum and these phonological processing areas were stronger than the connections between putamen and these areas. This pattern of results suggests that the putamen and cerebellum may have distinct roles in language processing. Based on research in the motor planning and control literature, we argue that the putamen engages in cortical initiation while the cerebellum amplifies and refines this signal to facilitate correct decision making.
Figures
References
-
- Abdullaev YG, Melnichuk KV. Cognitive operations in the human caudate nucleus. Neuroscience Letters. 1997;234(2–3):151–155. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, Delong MR, Strick PI. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 1986;9:357–381. - PubMed
-
- Barto AG, Fagg AH, Sitkoff N, Houk JC. A cerebellar model of timing and prediction in the control of reaching. Neural Computation. 1999;11(3):565–594. - PubMed
-
- Bechtereva NP, Abdullaev YG, Medvedev SV. Neuronal activity in frontal speech area 44 of the human cerebral cortex during word recognition. Neuroscience Letters. 1991;124(1):61–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

