Subcellular localization and function of alternatively spliced Noxo1 isoforms
- PMID: 17189824
- PMCID: PMC1868414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.08.024
Subcellular localization and function of alternatively spliced Noxo1 isoforms
Abstract
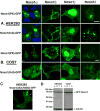
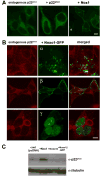
Nox organizer 1 (Noxo1), a p47(phox) homolog, is produced as four isoforms with unique N-terminal PX domains derived by alternative mRNA splicing. We compared the subcellular distribution of these isoforms or their isolated PX domains produced as GFP fusion proteins, as well as their ability to support Nox1 activity in several transfected models. Noxo1alpha, beta, gamma, and delta show different subcellular localization patterns, determined by their PX domains. In HEK293 cells, Noxo1beta exhibits prominent plasma membrane binding, Noxo1gamma shows plasma membrane and nuclear associations, and Noxo1alpha and delta localize primarily on intracellular vesicles or cytoplasmic aggregates, but not the plasma membrane. Nox1 activity correlates with Noxo1 plasma membrane binding in HEK293 cells, since Noxo1beta supports the highest activity and Noxo1gamma and Noxo1alpha support moderate or low activities, respectively. In COS-7 cells, where Noxo1alpha localizes on the plasma membrane, the activities supported by the three isoforms (alpha, beta, and gamma) do not differ significantly. The PX domains of beta and gamma bind the same phospholipids, including phosphatidic acid. These results indicate that the variant PX domains are unique determinants of Noxo1 localization and Nox1 function. Finally, the overexpressed Noxo1 isoforms do not affect p22(phox) localization, although Nox1 is needed to transport p22(phox) to the plasma membrane.
Figures


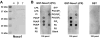

Comment in
-
The 'A's and 'O's of NADPH oxidase regulation: a commentary on "Subcellular localization and function of alternatively spliced Noxo1 isoforms".Free Radic Biol Med. 2007 Jan 15;42(2):175-9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.11.003. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007. PMID: 17189823 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Leto TL. Inflamation: basic principles and clinical correlates. In: Gallin JI, Snyderman R, editors. The respiratory burst oxidase. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1999. pp. 769–787.
-
- Babior BM. NADPH oxidase. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16:42–7. - PubMed
-
- Quinn MT, Gauss KA. Structure and regulation of the neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase: comparison with nonphagocyte oxidases. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76:760–81. - PubMed
-
- Lambeth JD. NOX enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4: 181–9. - PubMed
-
- Geiszt M, Leto TL. The Nox Family of NAD(P)H Oxidases: Host Defense and Beyond. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:51715–51718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

