Inhibitory complex of the transmembrane ammonia channel, AmtB, and the cytosolic regulatory protein, GlnK, at 1.96 A
- PMID: 17190799
- PMCID: PMC1765473
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0609796104
Inhibitory complex of the transmembrane ammonia channel, AmtB, and the cytosolic regulatory protein, GlnK, at 1.96 A
Abstract
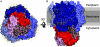
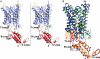
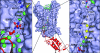
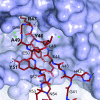
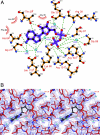
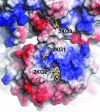
Ammonia conductance is highly regulated. A P(II) signal transduction protein, GlnK, is the final regulator of transmembrane ammonia conductance by the ammonia channel AmtB in Escherichia coli. The complex formed between AmtB and inhibitory GlnK at 1.96-A resolution shows that the trimeric channel is blocked directly by GlnK and how, in response to intracellular nitrogen status, the ability of GlnK to block the channel is regulated by uridylylation/deuridylylation at Y51. ATP and Mg(2+) augment the interaction of GlnK. The hydrolyzed product, adenosine 5'-diphosphate orients the surface of GlnK for AmtB blockade. 2-Oxoglutarate diminishes AmtB/GlnK association, and sites for 2-oxoglutarate are evaluated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Knepper MA, Packer R, Good DW. Physiol Rev. 1989;69:179–249. - PubMed
-
- Saier MH, Jr, Eng BH, Fard S, Garg J, Haggerty DA, Hutchinson WJ, Jack DL, Lai EC, Liu HJ, Nusinew DP, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1422:1–56. - PubMed
-
- Thomas GH, Mullins JG, Merrick M. Mol Microbiol. 2000;37:331–344. - PubMed
-
- Monfort P, Kosenko E, Erceg S, Canales JJ, Felipo V. Neurochem Int. 2002;41:95–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

