Nuclear IKK activity leads to dysregulated notch-dependent gene expression in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 17190815
- PMCID: PMC1765449
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0606476104
Nuclear IKK activity leads to dysregulated notch-dependent gene expression in colorectal cancer
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 8;105(14):5650
Abstract
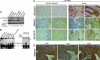
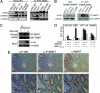
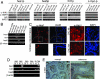
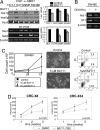
Nuclear functions for IkappaB kinase (IKK), including phosphorylation of histone H3 and nuclear corepressors, have been recently described. Here, we show that IKK is activated in colorectal tumors concomitant with the presence of phosphorylated SMRT (silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptor) corepressor that is aberrantly localized in the cytoplasm. In these tumors, IKKalpha associates to the chromatin of specific Notch targets, leading to the release of SMRT. Abrogation of IKK activity by BAY11-7082 or by expressing dominant negative IKKalpha restores the association of SMRT with Notch target genes, resulting in specific gene repression. Finally, BAY11-7082 significantly reduces tumor size in colorectal cancer xenografts (CRC-Xs) implanted in nude mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Trends Genet. 1993;9:138–141. - PubMed
-
- Su LK, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Preisinger AC, Moser AR, Luongo C, Gould KA, Dove WF. Science. 1992;256:668–670. - PubMed
-
- van Es JH, van Gijn ME, Riccio O, van den Born M, Vooijs M, Begthel H, Cozijnsen M, Robine S, Winton DJ, Radtke F, Clevers H. Nature. 2005;435:959–963. - PubMed
-
- Fre S, Huyghe M, Mourikis P, Robine S, Louvard D, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nature. 2005;435:964–968. - PubMed
-
- Leong KG, Karsan A. Blood. 2006;107:2223–2233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

