Somatic hypermutation: activation-induced deaminase for C/G followed by polymerase eta for A/T
- PMID: 17190841
- PMCID: PMC2118430
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20062409
Somatic hypermutation: activation-induced deaminase for C/G followed by polymerase eta for A/T
Abstract
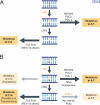
Somatic hypermutation (SHM) introduces nucleotide substitutions into immunoglobulin variable (Ig V) region genes at all four bases, but the mutations at C/G and A/T pairs are achieved by distinct mechanisms. Mutations at C/G pairs are a direct consequence of the C-->U deamination catalyzed by activation-induced deaminase (AID). Mutations at A/T pairs, however, require a second mutagenic process that occurs during patch repair of the AID-generated U/G mismatch. Several DNA polymerases have been proposed to play a role in SHM, but accumulating evidence indicates that the mutations at A/T are overwhelmingly achieved by recruitment of DNA polymerase eta.
Figures
Comment on
-
DNA polymerase eta is the sole contributor of A/T modifications during immunoglobulin gene hypermutation in the mouse.J Exp Med. 2007 Jan 22;204(1):17-23. doi: 10.1084/jem.20062131. Epub 2006 Dec 26. J Exp Med. 2007. PMID: 17190840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muramatsu M., K. Kinoshita, S. Fagarasan, S. Yamada, Y. Shinkai, and T. Honjo. 2000. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell. 102:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Revy, P., T. Muto, Y. Levy, F. Geissmann, A. Plebani, O. Sanal, N. Catalan, M. Forveille, R. Dufourcq-Labelouse, A. Gennery, et al. 2000. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) deficiency causes the autosomal recessive form of the Hyper-IgM syndrome (HIGM2). Cell. 102:565–575. - PubMed
-
- Rada, C., M.R. Ehrenstein, M.S. Neuberger, and C. Milstein. 1998. Hot spot focusing of somatic hypermutation in MSH2-deficient mice suggests two stages of mutational targeting. Immunity. 9:135–141. - PubMed
-
- Zeng, X., D.B. Winter, C. Kasmer, K.H. Kraemer, A.R. Lehmann, and P.J. Gearhart. 2001. DNA polymerase eta is an A-T mutator in somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin variable genes. Nat. Immunol. 2:537–541. - PubMed

