Pharmacological dissection and distribution of NaN/Nav1.9, T-type Ca2+ currents, and mechanically activated cation currents in different populations of DRG neurons
- PMID: 17190903
- PMCID: PMC2151607
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200609665
Pharmacological dissection and distribution of NaN/Nav1.9, T-type Ca2+ currents, and mechanically activated cation currents in different populations of DRG neurons
Abstract
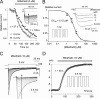
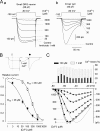
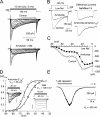
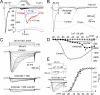
Low voltage-activated (LVA) T-type Ca(2+) (I(Ca)T) and NaN/Nav1.9 currents regulate DRG neurons by setting the threshold for the action potential. Although alterations in these channels have been implicated in a variety of pathological pain states, their roles in processing sensory information remain poorly understood. Here, we carried out a detailed characterization of LVA currents in DRG neurons by using a method for better separation of NaN/Nav1.9 and I(Ca)T currents. NaN/Nav1.9 was inhibited by inorganic I(Ca) blockers as follows (IC(50), microM): La(3+) (46) > Cd(2+) (233) > Ni(2+) (892) and by mibefradil, a non-dihydropyridine I(Ca)T antagonist. Amiloride, however, a preferential Cav3.2 channel blocker, had no effects on NaN/Nav1.9 current. Using these discriminative tools, we showed that NaN/Nav1.9, Cav3.2, and amiloride- and Ni(2+)-resistant I(Ca)T (AR-I(Ca)T) contribute differentially to LVA currents in distinct sensory cell populations. NaN/Nav1.9 carried LVA currents into type-I (CI) and type-II (CII) small nociceptors and medium-Adelta-like nociceptive cells but not in low-threshold mechanoreceptors, including putative Down-hair (D-hair) and Aalpha/beta cells. Cav3.2 predominated in CII-nociceptors and in putative D-hair cells. AR-I(Ca)T was restricted to CII-nociceptors, putative D-hair cells, and Aalpha/beta-like cells. These cell types distinguished by their current-signature displayed different types of mechanosensitive channels. CI- and CII-nociceptors displayed amiloride-sensitive high-threshold mechanical currents with slow or no adaptation, respectively. Putative D-hair and Aalpha/beta-like cells had low-threshold mechanical currents, which were distinguished by their adapting kinetics and sensitivity to amiloride. Thus, subspecialized DRG cells express specific combinations of LVA and mechanosensitive channels, which are likely to play a key role in shaping responses of DRG neurons transmitting different sensory modalities.
Figures








References
-
- Akopian, A.N., L. Sivilotti, and J.N. Wood. 1996. A tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel expressed by sensory neurons. Nature. 379:257–262. - PubMed
-
- Anderberg, M.R. 1973. Cluster Analysis for Applications. Academic Press, New York. 359 pp.
-
- Backx, P.H., D.T. Yue, J.H. Lawrence, E. Marban, and G.F. Tomaselli. 1992. Molecular localization of an ion-binding site within the pore of mammalian sodium channels. Science. 257:248–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

