Augmented generalized SENSE reconstruction to correct for rigid body motion
- PMID: 17191225
- PMCID: PMC3985846
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.21106
Augmented generalized SENSE reconstruction to correct for rigid body motion
Abstract
The correction of motion artifacts continues to be a significant problem in MRI. In the case of uncooperative patients, such as children, or patients who are unable to remain stationary, the accurate determination and correction of motion artifacts becomes a very important prerequisite for achieving good image quality. The application of conventional motion-correction strategies often produces inconsistencies in k-space data. As a result, significant residual artifacts can persist. In this work a formalism is introduced for parallel imaging in the presence of motion. The proposed method can improve overall image quality because it diminishes k-space inconsistencies by exploiting the complementary image encoding capacity of individual receiver coils. Specifically, an augmented version of an iterative SENSE reconstruction is used as a means of synthesizing the missing data in k-space. Motion is determined from low-resolution navigator images that are coregistered by an automatic registration routine. Navigator data can be derived from self-navigating k-space trajectories or in combination with other navigation schemes that estimate patient motion. This correction method is demonstrated by interleaved spiral images collected from volunteers. Conventional spiral scans and scans corrected with proposed techniques are shown, and the results illustrate the capacity of this new correction approach.
Figures




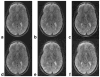
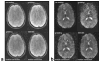

References
-
- Larkman DJ, Atkinson D, Hajnal JV. Artifact reduction using parallel imaging methods. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;15:267–275. - PubMed
-
- Pipe JG, Farthing VG, Forbes KP. Multishot diffusion-weighted FSE using PROPELLER MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2002;47:42–52. - PubMed
-
- Bydder M, Larkman DJ, Hajnal JV. Detection and elimination of motion artifacts by regeneration of k-space. Magn Reson Med. 2002;47:677– 686. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson D, Hill DL. Reconstruction after rotational motion. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49:183–187. - PubMed
-
- Bydder M, Atkinson D, Larkman DJ, Hill DL, Hajnal JV. SMASH navigators. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49:493–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

