Kawasaki disease
- PMID: 17191303
- PMCID: PMC2687814
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.6.759
Kawasaki disease
Abstract
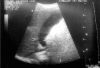
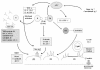
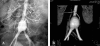
Kawasaki disease is an acute febrile, systemic vasculitic syndrome of an unknown etiology that primarily occurs in children younger than five years of age. The principal presentations of Kawasaki disease include fever, bilateral nonexudative conjunctivitis, erythema of the lips and oral mucosa, changes in the extremities, rash, and cervical lymphadenopathy. Coronary artery aneurysms or ectasia develops in 15% to 25% of untreated children with the disease, which may later lead to myocardial infarction, sudden death, or ischemic heart disease. Treatment with intravenous gamma globulin (IVIG) is effective, but the mode of action is still unclear. The development of a diagnostic test, a more specific therapy, and ultimately the prevention of this potentially fatal illness in children are all dependent upon the continued advances in determining the etiopathogenesis of this fascinating disorder.
Figures



References
-
- Kawasaki T. Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children [in Japanese] Arerugi. 1967;16:178–222. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T, Oya T, Watanabe A, et al. Clinical features of Kawasaki disease [in Japanese] Shonika Rinsho (Jpn J Pediatr) 1968;21:291–297.
-
- Kosaki F, Kawasaki T, Okawa S, et al. Clinicopathological conference on 10 fatal cases with acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome [in Japanese] Shonika Rinsho (Jpn J Pediatr) 1971;24:2545–2559.
-
- Kawasaki T, Kosaki F, Okawa S, Shigematsu I, Yanagawa H. A new infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) prevailing in Japan. Pediatrics. 1974;54:271–276. - PubMed
-
- Burns JC, Wiggins JW, Jr, Toews WH, Newburger JW, Leung DY, Wilson H, et al. Clinical spectrum of Kawasaki disease in infants younger than 6 months of age. J Pediatr. 1986;109:759–763. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

