A modified McCabe score for stratification of patients after intensive care unit discharge: the Sabadell score
- PMID: 17192174
- PMCID: PMC1794495
- DOI: 10.1186/cc5136
A modified McCabe score for stratification of patients after intensive care unit discharge: the Sabadell score
Abstract
Introduction: Mortality in the ward after an intensive care unit (ICU) stay is considered a quality parameter, and is described as a source of avoidable mortality. Additionally, the attending intensivist frequently anticipates fatal outcome after ICU discharge. Our objective was to test the ability of a new score to stratify patients according to ward mortality after ICU discharge.
Methods: A prospective cohort study was performed in the general ICU of a university-affiliated hospital. In 2003 and 2004 we prospectively recorded the attending intensivist's subjective prognosis at ICU discharge about the hospital outcome for each patient admitted to the ICU (the Sabadell score), which was later compared with the real hospital outcome.
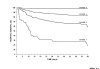
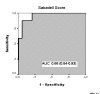
Results: We studied 1,521 patients with a mean age of 60.2 +/- 17.8 years. The median (25-75% percentile) ICU stay was five (three to nine) days. The ICU mortality was 23.8%, with 1,156 patients being discharged to the ward. Post-ICU ward mortality was 9.6%, mainly observed in patients with a Sabadell score of 3 (81.3%) or a score of 2 (41.1%), whereas lower mortality was observed in patients scoring 1 (17.2%) and scoring 0 (1.7%). Multivariate analysis selected age and the Sabadell score as the only variables associated with ward mortality, with an area under the receiver operating curve of 0.88 (95% CI 0.84-0.93) for the Sabadell score.
Conclusion: The Sabadell score at ICU discharge works effectively to stratify patients according to hospital outcome.
Figures
Comment in
-
Predicting mortality in intensive care unit survivors using a subjective scoring system.Crit Care. 2007;11(1):109. doi: 10.1186/cc5683. Crit Care. 2007. PMID: 17316458 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Tracheostomy tube in place at intensive care unit discharge is associated with increased ward mortality.Respir Care. 2009 Dec;54(12):1644-52. Respir Care. 2009. PMID: 19961629
-
Serum osmolality and outcome in intensive care unit patients.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006 Sep;50(8):970-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2006.01096.x. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006. PMID: 16923092
-
The acute physiology and chronic health evaluation III outcome prediction in patients admitted to the intensive care unit after pneumonectomy.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2007 Dec;21(6):832-7. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2006.12.005. Epub 2007 Mar 6. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2007. PMID: 18068061
-
Determinants of mortality after hospital discharge in ICU patients: literature review and Dutch cohort study.Crit Care Med. 2013 May;41(5):1237-51. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827ca4f9. Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23442988 Review.
-
Factors that predict outcome of intensive care treatment in very elderly patients: a review.Crit Care. 2005 Aug;9(4):R307-14. doi: 10.1186/cc3536. Epub 2005 May 17. Crit Care. 2005. PMID: 16137342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heterogenous treatment effect of neuromuscular blocking agents for moderate-to-severe ARDS: a post hoc Markov model re-analysis of the ACURASYS trial.Intensive Care Med. 2025 Aug 6. doi: 10.1007/s00134-025-08064-z. Online ahead of print. Intensive Care Med. 2025. PMID: 40768068
-
Predicting mortality in intensive care unit survivors using a subjective scoring system.Crit Care. 2007;11(1):109. doi: 10.1186/cc5683. Crit Care. 2007. PMID: 17316458 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Intensive Care Unit Readmission with Machine Learning Using Electronic Health Record Data.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018 Jul;15(7):846-853. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201710-787OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018. PMID: 29787309 Free PMC article.
-
Indications and Types of Antibiotic Agents Used in 6 Acute Care Hospitals, 2009-2010: A Pragmatic Retrospective Observational Study.Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2016 Jan;37(1):70-9. doi: 10.1017/ice.2015.226. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2016. PMID: 26456803 Free PMC article.
-
Ward mortality after ICU discharge: a multicenter validation of the Sabadell score.Intensive Care Med. 2010 Jul;36(7):1196-201. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1825-5. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Intensive Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20221748
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

