Proline-, glutamic acid-, and leucine-rich protein-1/modulator of nongenomic activity of estrogen receptor enhances androgen receptor functions through LIM-only coactivator, four-and-a-half LIM-only protein 2
- PMID: 17192406
- PMCID: PMC3725294
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2006-0269
Proline-, glutamic acid-, and leucine-rich protein-1/modulator of nongenomic activity of estrogen receptor enhances androgen receptor functions through LIM-only coactivator, four-and-a-half LIM-only protein 2
Abstract
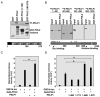
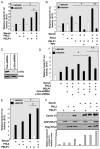
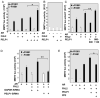
Proline-, glutamic acid-, and leucine-rich protein-1 (PELP1) is a coregulator of multiple nuclear receptors. Molecular mechanisms of PELP1 function are not completely understood, but its expression is up-regulated in hormonal-dependent cancers. Using a yeast two-hybrid screen, we found that four-and-a-half LIM-only protein 2 (FHL2) interacted with PELP1. FHL2 is a transcriptional regulator that associates with nuclear cofactors, including androgen receptors (ARs), and contains an intrinsic activation domain. PELP1 and FHL2 interact in vitro and in vivo and colocalize in the nuclear compartment. PELP1 interacts with FHL2 via LIM domains 3 and 4 and synergistically enhances the transcriptional activity of FHL2. Src kinase is required for PELP1-mediated enhancement of FHL2 functions because knockdown of Src kinase expression or function abolished PELP1-mediated FHL2 activation functions. PELP1 interacted with AR and enhanced FHL2-mediated AR transactivation functions. PELP1 knockdown by small interfering RNA or PELP1 mutant, which lacks an activation domain, reduced FHL2-mediated AR transactivation. Biochemical analyses revealed a complex consisting of PELP1, FHL2, and AR in prostate cancer cells. PELP1/MNAR expression was elevated in high-grade prostate tumors. Our results suggest that PELP1 functions as a molecular adaptor, coupling FHL2 with nuclear receptors, and PELP1-FHL2 interactions may have a role in prostate cancer progression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proline-, glutamic acid-, and leucine-rich protein-1 is essential in growth factor regulation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 activation.Cancer Res. 2005 Jul 1;65(13):5571-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4664. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15994929 Free PMC article.
-
PELP1: a review of PELP1 interactions, signaling, and biology.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Jan 25;382(1):642-651. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.07.031. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 23933151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic potential of the nuclear receptor coregulator proline-, glutamic acid-, leucine-rich protein 1/modulator of the nongenomic actions of the estrogen receptor.Cancer Res. 2007 Jun 1;67(11):5505-12. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3647. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17545633 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and biological properties of the nuclear receptor coregulator PELP1/MNAR.Nucl Recept Signal. 2007 May 17;5:e004. doi: 10.1621/nrs.05004. Nucl Recept Signal. 2007. PMID: 17525794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Androgen receptor coactivators lysine-specific histone demethylase 1 and four and a half LIM domain protein 2 predict risk of prostate cancer recurrence.Cancer Res. 2006 Dec 1;66(23):11341-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1570. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17145880
Cited by
-
Significance of PELP1 in ER-negative breast cancer metastasis.Mol Cancer Res. 2012 Jan;10(1):25-33. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0456. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Mol Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22086908 Free PMC article.
-
LAS1L interacts with the mammalian Rix1 complex to regulate ribosome biogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Feb;23(4):716-28. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-06-0530. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22190735 Free PMC article.
-
PELP1: A novel therapeutic target for hormonal cancers.IUBMB Life. 2010 Mar;62(3):162-9. doi: 10.1002/iub.287. IUBMB Life. 2010. PMID: 20014005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding extranuclear (nongenomic) androgen signaling: what a frog oocyte can tell us about human biology.Steroids. 2011 Aug;76(9):822-8. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2011.02.016. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Steroids. 2011. PMID: 21354434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-EM reveals the architecture of the PELP1-WDR18 molecular scaffold.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 9;13(1):6783. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34610-0. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36351913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vadlamudi RK, Wang RA, Mazumdar A, Kim Y, Shin J, Sahin A, Kumar R. Molecular cloning and characterization of PELP1, a novel human coregulator of estrogen receptor α. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:38272–38279. - PubMed
-
- Nair SS, Mishra SK, Yang Z, Balasenthil S, Kumar R, Vadlamudi RK. Potential role of a novel transcriptional coactivator PELP1 in histone H1 displacement in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6416–6423. - PubMed
-
- Vadlamudi RK, Balasenthil S, Broaddus RR, Gustafsson JA, Kumar R. Deregulation of estrogen receptor coactivator proline-, glutamic acid-, and leucine-rich protein-1/modulator of nongenomic activity of estrogen receptor in human endometrial tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:6130–6138. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

