Single-cell characterization of retrograde signaling by brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- PMID: 17192436
- PMCID: PMC6674723
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4576-06.2006
Single-cell characterization of retrograde signaling by brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Abstract
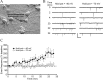
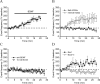
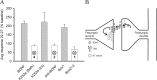
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a key regulator of hippocampal synaptic plasticity in the developing and adult nervous system. It can be released from pyramidal neuron dendrites in an activity-dependent manner and has therefore been suggested to serve as a signal that provides the retrograde intercellular communication necessary for Hebbian plasticity and hippocampal-dependent learning. Although much has been learned about BDNF function by field stimulation of hippocampal neurons, it is not known whether moderate action potential-independent depolarization of single cells is capable of releasing sufficient BDNF to influence transmission at individual synapses. In this study, we show directly at the single-cell level that such modulation can occur. By using K-252a, anti-BDNF antibody, and interruption of regulated release, we confirm a model in which postsynaptic depolarization elicits calcium-dependent release of BDNF that diffuses retrogradely and enhances presynaptic transmitter release.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Presynaptic modulation of synaptic transmission and plasticity by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the developing hippocampus.J Neurosci. 1998 Sep 1;18(17):6830-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-17-06830.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9712654 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent Wnt 7 dendritic targeting in hippocampal neurons: plasticity- and tagging-related retrograde signaling mechanism?Hippocampus. 2014 Apr;24(4):455-65. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22239. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Hippocampus. 2014. PMID: 24375790
-
BDNF up-regulates evoked GABAergic transmission in developing hippocampus by potentiating presynaptic N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channels signalling.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Dec;16(12):2297-310. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02313.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12492424
-
Neurotrophin-dependent modulation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the mammalian CNS.Gen Pharmacol. 1998 Nov;31(5):667-74. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(98)00190-6. Gen Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9809461 Review.
-
Regulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity by BDNF.Brain Res. 2015 Sep 24;1621:82-101. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.019. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25451089 Review.
Cited by
-
BDNF over-expression increases olfactory bulb granule cell dendritic spine density in vivo.Neuroscience. 2015 Sep 24;304:146-60. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.056. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26211445 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF signaling in the formation, maturation and plasticity of glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses.Exp Brain Res. 2009 Dec;199(3-4):203-34. doi: 10.1007/s00221-009-1994-z. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Exp Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19777221 Review.
-
The depolarizing action of GABA controls early network activity in the developing hippocampus.Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Apr;43(2):97-106. doi: 10.1007/s12035-010-8147-z. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21042953 Review.
-
Wiring and firing neuronal networks: endocannabinoids take center stage.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008 Jun;18(3):338-45. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.08.007. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18801434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABA(B) receptor activation triggers BDNF release and promotes the maturation of GABAergic synapses.J Neurosci. 2009 Sep 16;29(37):11650-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3587-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19759312 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
