Extracellular hippocampal acetylcholine level controls amygdala function and promotes adaptive conditioned emotional response
- PMID: 17192439
- PMCID: PMC6674713
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3713-06.2006
Extracellular hippocampal acetylcholine level controls amygdala function and promotes adaptive conditioned emotional response
Abstract
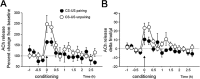
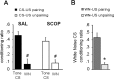
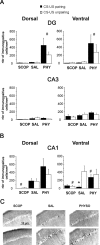
Ample data indicate that tone and contextual fear conditioning differentially require the amygdala and the hippocampus. However, mechanisms subserving the adaptive selection among environmental stimuli (discrete tone vs context) of those that best predict an aversive event are still elusive. Because the hippocampal cholinergic neurotransmission is thought to play a critical role in the coordination between different memory systems leading to the selection of appropriate behavioral strategies, we hypothesized that this cholinergic signal may control the competing acquisition of amygdala-mediated tone and contextual conditioning. Using pavlovian fear conditioning in mice, we first show a higher level of hippocampal acetylcholine release and a specific pattern of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) activation within the lateral (LA) and basolateral (BLA) amygdala under conditions in which the context is a better predictor than a discrete tone stimulus. Second, we demonstrate that levels of hippocampal cholinergic neurotransmission are causally related to the patterns of ERK1/2 activation in amygdala nuclei and actually determine the selection among the context or the simple tone the stimulus that best predicts the aversive event. Specifically, decreasing the hippocampal cholinergic signal not only impaired contextual conditioning but also mimicked conditioning to the discrete tone, both in terms of the behavioral outcome and the LA/BLA ERK1/2 activation pattern. Conversely, increasing this cholinergic signal not only disrupted tone conditioning but also promoted contextual fear conditioning. Hence, these findings highlight that hippocampal cholinergic neurotransmission controls amygdala function, thereby leading to the selection of relevant emotional information.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential modulation of changes in hippocampal-septal synaptic excitability by the amygdala as a function of either elemental or contextual fear conditioning in mice.J Neurosci. 1998 Jan 1;18(1):480-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-01-00480.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9412524 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation of amygdaloid and hippocampal auditory-evoked potentials in a discriminatory fear-conditioning task in mice as a function of tone pattern and context.Eur J Neurosci. 2003 Aug;18(3):639-50. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02758.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12911760
-
A different recruitment of the lateral and basolateral amygdala promotes contextual or elemental conditioned association in Pavlovian fear conditioning.Learn Mem. 2005 Jul-Aug;12(4):383-8. doi: 10.1101/lm.92305. Epub 2005 Jul 18. Learn Mem. 2005. PMID: 16027178 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive emotional memory: the key hippocampal-amygdalar interaction.Stress. 2015;18(3):297-308. doi: 10.3109/10253890.2015.1067676. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Stress. 2015. PMID: 26260664 Review.
-
Pavlovian fear conditioning as a behavioral assay for hippocampus and amygdala function: cautions and caveats.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Oct;28(8):1661-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06485.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18973583 Review.
Cited by
-
Dorsal hippocampal NMDA receptor blockade impairs extinction of naloxone-precipitated conditioned place aversion in acute morphine-treated rats by suppressing ERK and CREB phosphorylation in the basolateral amygdala.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(2):482-91. doi: 10.1111/bph.12671. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24597568 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociated roles for the lateral and medial septum in elemental and contextual fear conditioning.Learn Mem. 2007 Jun 6;14(6):422-9. doi: 10.1101/lm.531407. Print 2007 Jun. Learn Mem. 2007. PMID: 17554087 Free PMC article.
-
The role of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in fear and extinction memory.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016 Sep;133:39-52. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27264248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basal forebrain cholinergic systems as circuits through which traumatic stress disrupts emotional memory regulation.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024 Apr;159:105569. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105569. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024. PMID: 38309497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bilateral phosphorylation of ERK in the lateral and centrolateral amygdala during unilateral storage of fear memories.Neuroscience. 2009 Dec 15;164(3):908-17. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.08.071. Epub 2009 Sep 6. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19735699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Gale GD, Fanselow MS. Hippocampus and contextual fear conditioning: recent controversies and advances. Hippocampus. 2001;11:8–17. - PubMed
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman DM, Rawlins JN, McHugh SB, Deacon RM, Yee BK, Bast T, Zhang WN, Pothuizen HH, Feldon J. Regional dissociations within the hippocampus: memory and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;28:273–283. - PubMed
-
- Bast T, Zhang WN, Feldon J. Dorsal hippocampus and classical fear conditioning to tone and context in rats: effects of local NMDA-receptor blockade and stimulation. Hippocampus. 2003;13:657–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
