Effects of nitric oxide on bovine polymorphonuclear functions
- PMID: 17193882
- PMCID: PMC1636001
Effects of nitric oxide on bovine polymorphonuclear functions
Abstract
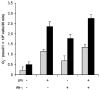
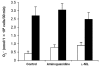
The effects of nitric oxide (NO) on the functionality of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) in bovine milk or blood were investigated. In 2 experiments, mastitis was induced by infusing both hind quarters with saline containing Escherichia coli endotoxins. In addition, the left hind quarter was infused with aminoguanidine, an inhibitor of the inducible form of NO synthase (iNOS). At various times after infusion, somatic cells were isolated from milk samples, and superoxide (O2-) production induced by phorbol myristate acetate was evaluated. In both experiments, the addition of aminoguanidine had no inhibitory effect on the number of milk somatic cells or on their O2- production. The effect of NO and iNOS inhibitors on the functionality of bovine PMNs isolated from blood was investigated in vitro. The neutrophils did not produce NO. A neutrophil:monocyte co-culture system was used to study the effect of NO derived from monocytes on O2- production by bovine neutrophils. Neither NO derived from activated monocytes nor the iNOS inhibitors aminoguanidine and L-N6-(1-iminoethyl)lysine had an effect on the ability of bovine neutrophils to release O2-. Moreover, aminoguanidine did not affect the ability of bovine neutrophils to phagocytose bacteria. These results suggest that inhibition of NO release during inflammation does not interfere with the migration of immune cells to the site of infection or the ability of these cells to destroy pathogens. Thus, NO does not appear to play a major role in the control of the functions of bovine neutrophils.
Les effets du monoxyde d’azote (NO) sur la fonctionnalité de neutrophiles (PMNs) bovins isolés du lait ou du sang ont été investigués. Lors de deux expériences, une mammite a été induite par l’infusion d’endotoxine d’Escherichia coli dans les quartiers arrières de vaches laitières. De plus, le quartier arrière gauche a été infusé avec de l’aminoguanidine, un inhibiteur de la forme inductible de l’enzyme produisant le monoxyde d’azote (iNOS). La production d’anion superoxyde a été évaluée chez des cellules somatiques isolées du lait et stimulées ou non avec du phorbol myristate acétate. Aucun effet inhibiteur de l’aminoguanidine n’a été observé sur l’augmentation des cellules somatiques du lait et sur la production d’anion superoxyde. Les effets du NO et d’inhibiteurs de sa synthèse sur des PMNs isolés du sang ont été investigués in vitro. Les PMNs n’ont pas produit de NO. Une co-culture neutrophiles:monocytes a été utilisée afin de vérifier l’effet NO produit par les monocytes sur la production d’anion superoxyde par les neutrophiles. Ni le NO produit par les monocytes ni les inhibiteurs aminoguanidine et
(Traduit par les auteurs)
Figures

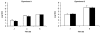



Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide production during endotoxin-induced mastitis in the cow.J Dairy Sci. 1999 Dec;82(12):2574-81. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(99)75512-8. J Dairy Sci. 1999. PMID: 10629803
-
Induction of nitric oxide production by bovine mammary epithelial cells and blood leukocytes.J Dairy Sci. 2001 Jun;84(6):1430-7. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(01)70175-0. J Dairy Sci. 2001. PMID: 11417702
-
Effect of bovine neutrophil maturity on phagocytosis.Am J Vet Res. 1976 Jun;37(6):703-5. Am J Vet Res. 1976. PMID: 779542
-
Modulation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes function by nitric oxide.Thromb Res. 2000 Nov 1;100(3):223-47. doi: 10.1016/s0049-3848(00)00320-0. Thromb Res. 2000. PMID: 11108909 Review.
-
Role of neutrophil polymorphonuclear leukocytes during bovine coliform mastitis: physiology or pathology?Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2004;66(2):97-150; discussion 150-3. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2004. PMID: 15074078 Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil recruitment in endotoxin-induced murine mastitis is strictly dependent on mammary alveolar macrophages.Vet Res. 2010 Jan-Feb;41(1):10. doi: 10.1051/vetres/2009058. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Vet Res. 2010. PMID: 19828114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paape MJ, Shafer-Weaver K, Capuco AV, Van Oostveldt K, Burvenich C. Immune surveillance of mammary tissue by phagocytic cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;480:259–277. - PubMed
-
- Heyneman R, Burvenich C, Vercauteren R. Interaction between respiratory burst activity of neutrophil leukocytes and experimentally induced Escherichia coli mastitis in cows. J Dairy Sci. 1990;73:985–994. - PubMed
-
- Fridovich I. Superoxide radical: an endogenous toxicant. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:239–257. - PubMed
-
- Poch B, Gansauge F, Rau B, et al. The role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and oxygen-derived free radicals in experimental acute pancreatitis: mediators of local destruction and activators of inflammation. FEBS Lett. 1999;461:268–272. - PubMed
-
- Jones OTG. The regulation of superoxide production by the NADPH oxidase of neutrophils and other mammalian cells. Bioessays. 1994;16:919–923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
