Pharmacokinetics and milk penetration of ibafloxacin after intravenous administration to lactating goats
- PMID: 17193885
- PMCID: PMC1635999
Pharmacokinetics and milk penetration of ibafloxacin after intravenous administration to lactating goats
Abstract
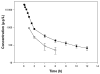
The pharmacokinetic behavior of ibafloxacin was studied after intravenous administration of a single dose of 15 mg/kg to 6 healthy lactating goats. Plasma concentrations of ibafloxacin were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. The data for concentration versus time could best be described by a 2-compartment model. The mean plasma ibafloxacin clearance (and standard error) was 1.05 (0.10) L/h x kg. The mean steady-state volume of distribution was 1.65 (0.42) L/kg. The mean elimination half-life was 3.76 (0.30) h. Ibafloxacin penetration from the blood to the milk was poor. The ratio between the areas under the concentration-time curve of milk and plasma was 0.20 (0.01), indicating scant penetration of ibafloxacin into the milk.
Les propriétés pharmacocinétiques de l’ibafloxacine ont été étudiées après administration intraveineuse d’une dose unique de 15 mg/kg à six chèvres en santé en lactation. Les concentrations plasmatiques d’ibafloxacine ont été mesurées par chromatographie en phase liquide à haute performance avec détection par fluorescence. Les données de la concentration en fonction du temps peuvent être le mieux décrites par un modèle à 2 compartiments. La clairance plasmatique moyenne d’ibafloxacine (et l’erreur type) était 1,05 (0,10) L/h·kg. Le volume moyen de distribution à l’équilibre dynamique était 1,65 (0,42) L/kg. La demi-vie moyenne d’élimination était 3,76 (0,30) h. La pénétration d’ibafloxacine du sang vers le lait était faible. Le ratio entre les surfaces sous la courbe de la relation concentration–temps du sang et du plasma était 0,20 (0,01), indiquant une pénétration peu marquée de l’ibafloxacine dans le lait.
(Traduit par Docteur Serge Messier)
Figures
References
-
- Coulet M, van Borssum Waalkes M, Cox P, Lohuis J. In vitro and in vivo pharmacodynamic properties of the fluoroquinolone ibafloxacin. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2002;25:401–411. - PubMed
-
- Walker RD. Fluoroquinolones. In: Prescott JF, Baggot JD, Walker RD, eds. Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary Medicine. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press, 2000:315–338.
-
- Fernández-Varón E, Villamayor L, Escudero E, Espuny A, Cárceles CM. Pharmacokinetics and milk penetration of moxifloxacin after intravenous and subcutaneous administration to lactating goats. Vet J. 2006;172:302–307. - PubMed
-
- Abo El-Sooud K. Influence of albendazole on the disposition kinetics and milk antimicrobial equivalent activity of enrofloxacin in lactating goats. Pharmacol Res. 2003;48:389–395. - PubMed
-
- Abd El-Aty AM, Goudah A. Some pharmacokinetic parameters of pefloxacin in lactating goats. Vet Res Commun. 2002;26:553–561. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources