Transcriptional regulation of the Drosophila melanogaster muscle myosin heavy-chain gene
- PMID: 17194628
- PMCID: PMC2002476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.modgep.2006.11.007
Transcriptional regulation of the Drosophila melanogaster muscle myosin heavy-chain gene
Abstract
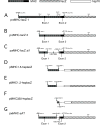
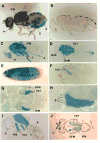
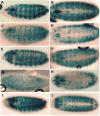
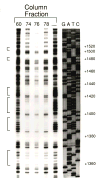
We show that a 2.6kb fragment of the muscle myosin heavy-chain gene (Mhc) of Drosophila melanogaster (containing 458 base pairs of upstream sequence, the first exon, the first intron and the beginning of the second exon) drives expression in all muscles. Comparison of the minimal promoter to Mhc genes of 10 Drosophila species identified putative regulatory elements in the upstream region and in the first intron. The first intron is required for expression in four small cells of the tergal depressor of the trochanter (jump) muscle and in the indirect flight muscle. The 3'-end of this intron is important for Mhc transcription in embryonic body wall muscle and contains AT-rich elements that are protected from DNase I digestion by nuclear proteins of Drosophila embryos. Sequences responsible for expression in embryonic, adult body wall and adult head muscles are present both within and outside the intron. Elements important for expression in leg muscles and in the large cells of the jump muscle flank the intron. We conclude that multiple transcriptional regulatory elements are responsible for Mhc expression in specific sets of Drosophila muscles.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmental regulation of the Drosophila tropomyosin II gene in different muscles is controlled by muscle-type-specific intron enhancer elements and distal and proximal promoter control elements.Dev Biol. 1993 Oct;159(2):500-12. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1259. Dev Biol. 1993. PMID: 8405674
-
Developmental regulation of the Drosophila Tropomyosin I (TmI) gene is controlled by a muscle activator enhancer region that contains multiple cis-elements and binding sites for multiple proteins.Dev Genet. 1997;20(4):297-306. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6408(1997)20:4<297::AID-DVG1>3.0.CO;2-2. Dev Genet. 1997. PMID: 9254904
-
Splice-junction elements and intronic sequences regulate alternative splicing of the Drosophila myosin heavy chain gene transcript.Genetics. 1997 Oct;147(2):725-41. doi: 10.1093/genetics/147.2.725. Genetics. 1997. PMID: 9335608 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinate regulation of Drosophila tropomyosin gene expression is controlled by multiple muscle-type-specific positive and negative enhancer elements.Dev Biol. 1993 Oct;159(2):513-27. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1260. Dev Biol. 1993. PMID: 8405675
-
Determining structure/function relationships for sarcomeric myosin heavy chain by genetic and transgenic manipulation of Drosophila.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Sep 15;50(6):430-42. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20000915)50:6<430::AID-JEMT2>3.0.CO;2-E. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10998634 Review.
Cited by
-
A single-cell atlas of the Culex tarsalis midgut during West Nile virus infection.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 24:2024.07.23.603613. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.23.603613. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jan 27;21(1):e1012855. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012855. PMID: 39091762 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A population of adult satellite-like cells in Drosophila is maintained through a switch in RNA-isoforms.Elife. 2018 Apr 9;7:e35954. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35954. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29629869 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Inhibited Smooth Muscle Myosin and Its Implications on the Regulation of Insect Striated Muscle Myosin.Life (Basel). 2025 Feb 27;15(3):379. doi: 10.3390/life15030379. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40141724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intron and 5' distal region of the soybean Gmubi promoter contribute to very high levels of gene expression in transiently and stably transformed tissues.Plant Cell Rep. 2015 Jan;34(1):111-20. doi: 10.1007/s00299-014-1691-7. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Plant Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25292438
-
Screening and Verification of Molecular Markers and Genes Related to Salt-Alkali Tolerance in Portunus trituberculatus.Front Genet. 2022 Feb 8;13:755004. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.755004. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35211153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arredondo JJ, Ferreres RM, Maroto M, Cripps RM, Marco R, Bernstein SI, Cervera M. Control of Drosophila paramyosin/miniparamyosin gene expression. Differential regulatory mechanisms for muscle-specific transcription. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:8278–8287. - PubMed
-
- Basi GS, Storti RV. Structure and DNA sequence of the tropomyosin I gene from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:817–827. - PubMed
-
- Bernard F, Dutriaux A, Silber J, Lalouette A. Notch pathway repression by vestigial is required to promote indirect flight muscle differentiation in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 2006;295:164–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

