Comparative genomics and adaptive selection of the ATP-binding-cassette gene family in caenorhabditis species
- PMID: 17194779
- PMCID: PMC1840077
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.066720
Comparative genomics and adaptive selection of the ATP-binding-cassette gene family in caenorhabditis species
Abstract
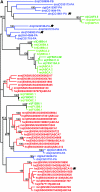
ABC transporters constitute one of the largest gene families in all species. They are mostly involved in transport of substrates across membranes. We have previously demonstrated that the Caenorhabditis elegans ABC family shows poor one-to-one gene orthology with other distant model organisms. To address the evolution dynamics of this gene family among closely related species, we carried out a comparative analysis of the ABC family among the three nematode species C. elegans, C. briggsae, and C. remanei. In contrast to the previous observations, the majority of ABC genes in the three species were found in orthologous trios, including many tandemly duplicated ABC genes, indicating that the gene duplication took place before speciation. Species-specific expansions of ABC members are rare and mostly observed in subfamilies A and B. C. briggsae and C. remanei orthologous ABC genes tend to cluster on trees, with those of C. elegans as an outgroup, consistent with their proposed species phylogeny. Comparison of intron/exon structures of the highly conserved ABCE subfamily members also indicates a closer relationship between C. briggsae and C. remanei than between either of these species and C. elegans. A comparison between insect and mammalian species indicates lineage-specific duplications or deletions of ABC genes, while the family size remains relatively constant. Sites undergoing positive selection within subfamily D, which are implicated in very-long-chain fatty acid transport, were identified. The evolution of these sites might be driven by the changes in food source with time.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of function and interaction of transcription factors in nematodes: extensive conservation of orthology coupled to rapid sequence evolution.BMC Genomics. 2008 Aug 27;9:399. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-399. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18752680 Free PMC article.
-
The Caenorhabditis globin gene family reveals extensive nematode-specific radiation and diversification.BMC Evol Biol. 2008 Oct 9;8:279. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-279. BMC Evol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18844991 Free PMC article.
-
The ABC transporter gene family of Daphnia pulex.BMC Genomics. 2009 Apr 21;10:170. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-170. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19383151 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter and heavy metal associated (HMA) gene families in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.).BMC Genomics. 2020 Oct 19;21(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07121-9. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33076828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ABC gene family in arthropods: comparative genomics and role in insecticide transport and resistance.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Feb;45:89-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24291285 Review.
Cited by
-
The same or not the same: lineage-specific gene expansions and homology relationships in multigene families in nematodes.J Mol Evol. 2015 Jan;80(1):18-36. doi: 10.1007/s00239-014-9651-y. Epub 2014 Oct 17. J Mol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25323991
-
Gene expression analysis of ABC transporters in a resistant Cooperia oncophora isolate following in vivo and in vitro exposure to macrocyclic lactones.Parasitology. 2013 Apr;140(4):499-508. doi: 10.1017/S0031182012001849. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Parasitology. 2013. PMID: 23279803 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative genomic analysis of the small heat shock proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans and briggsae.Genetica. 2008 Jul;133(3):307-19. doi: 10.1007/s10709-007-9215-9. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Genetica. 2008. PMID: 17940840
-
The cystic-fibrosis-associated ΔF508 mutation confers post-transcriptional destabilization on the C. elegans ABC transporter PGP-3.Dis Model Mech. 2012 Nov;5(6):930-9. doi: 10.1242/dmm.008987. Epub 2012 May 8. Dis Model Mech. 2012. PMID: 22569626 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of hookworm DAF-16/FOXO response elements and direct gene targets.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 19;5(8):e12289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012289. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20808816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambudkar, S. V., S. Dey, C. A. Hrycyna, M. Ramachandra, I. Pastan et al., 1999. Biochemical, cellular, and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 39: 361–398. - PubMed
-
- Burge, C. B., and S. Karlin, 1997. Prediction of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 268: 78–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

