Experimental Fasciola hepatica infection alters responses to tests used for diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis
- PMID: 17194810
- PMCID: PMC1828587
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01445-06
Experimental Fasciola hepatica infection alters responses to tests used for diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis
Abstract
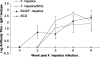
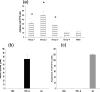
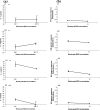
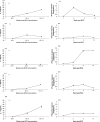
Fasciola hepatica is a prevalent helminth parasite of livestock. Infection results in polarization of the host's immune response and generation of type 2 helper (Th2) immune responses, which are known to be inhibitory to Th1 responses. Bovine tuberculosis (BTB) is a bacterial disease of economic and zoonotic importance. Control polices for this disease rely on extensive annual testing and a test-and-slaughter policy. The correct diagnosis of BTB relies on cell-mediated immune responses. We established a model of coinfection of F. hepatica and Mycobacterium bovis BCG to examine the impact of helminth infection on correct diagnosis. We found the predictive capacity of tests to be compromised in coinfected animals and that F. hepatica infection altered macrophage function. Interleukin-4 and gamma interferon expression in whole-blood lymphocytes restimulated in vitro with M. bovis antigen was also altered in coinfected animals. These results raise the question of whether F. hepatica infection can affect the predictive capacity of tests for the diagnosis of BTB and possibly also influence susceptibility to BTB and other bacterial diseases. Further studies on the interplay between helminth infection and BTB are warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fasciola hepatica infection reduces Mycobacterium bovis burden and mycobacterial uptake and suppresses the pro-inflammatory response.Parasite Immunol. 2016 Jul;38(7):387-402. doi: 10.1111/pim.12326. Parasite Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27108767 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Infection of cattle with Fasciola hepatica and Mycobacterium bovis- immunological consequences.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2009 Aug;56(6-7):269-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1865-1682.2009.01075.x. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2009. PMID: 19575746
-
Liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) co-infection with bovine tuberculosis (bTB) in cattle: A retrospective animal-level assessment of bTB risk in dairy and beef cattle.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019 Mar;66(2):785-796. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13083. Epub 2018 Dec 23. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019. PMID: 30484969
-
Co-infection of cattle with Fasciola hepatica or F. gigantica and Mycobacterium bovis: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 30;14(12):e0226300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226300. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31887151 Free PMC article.
-
The immunoregulatory effects of co-infection with Fasciola hepatica: From bovine tuberculosis to Johne's disease.Vet J. 2017 Apr;222:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Vet J. 2017. PMID: 28410676 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune signatures of pathogenesis in the peritoneal compartment during early infection of sheep with Fasciola hepatica.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 5;7(1):2782. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03094-0. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28584245 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies and Inflammation: Fecal Biomarkers of Gut Health in Domestic Ruminants.J Exp Zool A Ecol Integr Physiol. 2025 May;343(4):468-479. doi: 10.1002/jez.2896. Epub 2025 Jan 22. J Exp Zool A Ecol Integr Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39840509 Free PMC article.
-
Major secretory antigens of the helminth Fasciola hepatica activate a suppressive dendritic cell phenotype that attenuates Th17 cells but fails to activate Th2 immune responses.Infect Immun. 2010 Feb;78(2):793-801. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00573-09. Epub 2009 Nov 16. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 19917714 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L2 negatively regulates Th1-mediated immunopathology during Fasciola hepatica infection.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 22;7(47):77721-77731. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12790. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27783986 Free PMC article.
-
Fasciola hepatica infection reduces Mycobacterium bovis burden and mycobacterial uptake and suppresses the pro-inflammatory response.Parasite Immunol. 2016 Jul;38(7):387-402. doi: 10.1111/pim.12326. Parasite Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27108767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aida, Y., and M. J. Pabst. 1990. Removal of endotoxin from protein solutions by phase separation using Triton X-114. J. Immunol. Methods 132:191-195. - PubMed
-
- Aitken, M. M., P. W. Jones, G. A. Hall, D. L. Hughes, and K. A. Collis. 1978. Effects of experimental Salmonella dublin infection in cattle given Fasciola hepatica thirteen weeks previously. J. Comp. Pathol. 88:75-84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

