Analysis of rice glycosyl hydrolase family 1 and expression of Os4bglu12 beta-glucosidase
- PMID: 17196101
- PMCID: PMC1781453
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-6-33
Analysis of rice glycosyl hydrolase family 1 and expression of Os4bglu12 beta-glucosidase
Abstract
Background: Glycosyl hydrolase family 1 (GH1) beta-glucosidases have been implicated in physiologically important processes in plants, such as response to biotic and abiotic stresses, defense against herbivores, activation of phytohormones, lignification, and cell wall remodeling. Plant GH1 beta-glucosidases are encoded by a multigene family, so we predicted the structures of the genes and the properties of their protein products, and characterized their phylogenetic relationship to other plant GH1 members, their expression and the activity of one of them, to begin to decipher their roles in rice.
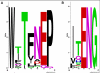
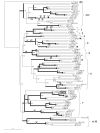
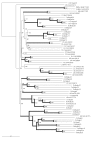
Results: Forty GH1 genes could be identified in rice databases, including 2 possible endophyte genes, 2 likely pseudogenes, 2 gene fragments, and 34 apparently competent rice glycosidase genes. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that GH1 members with closely related sequences have similar gene structures and are often clustered together on the same chromosome. Most of the genes appear to have been derived from duplications that occurred after the divergence of rice and Arabidopsis thaliana lineages from their common ancestor, and the two plants share only 8 common gene lineages. At least 31 GH1 genes are expressed in a range of organs and stages of rice, based on the cDNA and EST sequences in public databases. The cDNA of the Os4bglu12 gene, which encodes a protein identical at 40 of 44 amino acid residues with the N-terminal sequence of a cell wall-bound enzyme previously purified from germinating rice, was isolated by RT-PCR from rice seedlings. A thioredoxin-Os4bglu12 fusion protein expressed in Escherichia coli efficiently hydrolyzed beta-(1,4)-linked oligosaccharides of 3-6 glucose residues and laminaribiose.
Conclusion: Careful analysis of the database sequences produced more reliable rice GH1 gene structure and protein product predictions. Since most of these genes diverged after the divergence of the ancestors of rice and Arabidopsis thaliana, only a few of their functions could be implied from those of GH1 enzymes from Arabidopsis and other dicots. This implies that analysis of GH1 enzymes in monocots is necessary to understand their function in the major grain crops. To begin this analysis, Os4bglu12 beta-glucosidase was characterized and found to have high exoglucanase activity, consistent with a role in cell wall metabolism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A stress-induced rice (Oryza sativa L.) beta-glucosidase represents a new subfamily of glycosyl hydrolase family 5 containing a fascin-like domain.Biochem J. 2007 Dec 1;408(2):241-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070734. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17705786 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and expression analysis of glycosyl hydrolase family 35 genes from rice (Oryza sativa L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2008 Jul 30;8:84. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-8-84. BMC Plant Biol. 2008. PMID: 18664295 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary expansion, gene structure, and expression of the rice wall-associated kinase gene family.Plant Physiol. 2005 Nov;139(3):1107-24. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.069005. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16286450 Free PMC article.
-
The endo-beta-mannanase gene families in Arabidopsis, rice, and poplar.Funct Integr Genomics. 2007 Jan;7(1):1-16. doi: 10.1007/s10142-006-0034-3. Epub 2006 Aug 8. Funct Integr Genomics. 2007. PMID: 16897088 Review.
-
β-Glucosidases: Multitasking, moonlighting or simply misunderstood?Plant Sci. 2015 Dec;241:246-59. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.10.014. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26706075 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of quantitative trait loci for resistance to shoot fly in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench].Theor Appl Genet. 2009 Nov;119(8):1425-39. doi: 10.1007/s00122-009-1145-8. Epub 2009 Sep 18. Theor Appl Genet. 2009. PMID: 19763534
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of active ingredients related β-Glucosidases in Dendrobium catenatum.BMC Genomics. 2022 Aug 23;23(1):612. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08840-x. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35999493 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous Application of Phytohormones Promotes Growth and Regulates Expression of Wood Formation-Related Genes in Populus simonii × P. nigra.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 12;20(3):792. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030792. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30759868 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genes involved in cell wall biogenesis in grasses by differential gene expression profiling of elongating and non-elongating maize internodes.J Exp Bot. 2011 Jun;62(10):3545-61. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err045. Epub 2011 Mar 14. J Exp Bot. 2011. PMID: 21402660 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the Transcriptomics of Oil Palm Seed Germination.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 24;13(19):2680. doi: 10.3390/plants13192680. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fowler T. Deletion of the Trichoderma reesei β-glucosidase gene, bgl1. In: Esen A, editor. β-glucosidases: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Washington DC: American Chemical Society; 1993. pp. 56–65. [ACS Symposium Series 533]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

