Health-related quality of life in patients with chronic hepatitis C and advanced fibrosis
- PMID: 17196293
- PMCID: PMC1995129
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2006.10.009
Health-related quality of life in patients with chronic hepatitis C and advanced fibrosis
Abstract
Background/aims: Although the antiviral and histological benefits of peginterferon/ribavirin therapy are well established, the effects on health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and sexual health are less certain. This study assessed HRQOL and sexual health in patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis in the HALT-C Trial.
Methods: Subjects completed SF-36 and sexual health questionnaires prior to and after 24 weeks of peginterferon/ribavirin therapy (n=1144). Three hundred and seventy-three (33%) subjects were HCV RNA negative at week 20 and continued therapy through week 48; 258 were seen at week 72. One hundred and eighty achieved sustained virological responses (SVR) and 78 relapsed.
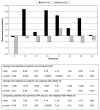
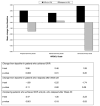
Results: At baseline, patients had poorer scores for all eight SF-36 domains compared to healthy controls. Patients with cirrhosis had lower HRQOL scores than those with bridging fibrosis, as did patients with higher depression scores. SVR patients had significant improvements in seven domains, whereas relapsers had significant worsening in one domain. Sexual scores improved in SVR patients and decreased in relapsers (p=0.03). In multivariate analyses, improvements in HRQOL and sexual scores were significantly associated with SVR but were less striking in patients with lower depression scores.
Conclusions: Achievement of SVR after peginterferon/ribavirin therapy improves HRQOL and sexual health in chronic hepatitis C patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis.
Figures


References
-
- Liang TJ, Rehermann B, Seeff LB, Hoofnagle JH. Pathogenesis, natural history, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis C. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132:296–305. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong GL, Wasley A, Simard EP, McQuillan GM, Kuhnert WL, Alter MJ. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:705–714. - PubMed
-
- Hoofnagle JH. Hepatitis C: the clinical spectrum of disease. Hepatology. 1997;26 (3 Suppl 1):15S–20S. - PubMed
-
- Di Bisceglie AM, Hoofnagle JH. Optimal therapy of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002;36 (5 Suppl 1):S121–S127. - PubMed
-
- National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement. Management of hepatitis C: 2002–June 10–12, 2002. Hepatology. 2002;36(5 Suppl 1):S3–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-DK-9-2325/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2328/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2318/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2319/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2321/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2327/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2320/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2326/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2322/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2323/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-06192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

