Acetylcholinesterase: converting a vulnerable target to a template for antidotes and detection of inhibitor exposure
- PMID: 17196318
- PMCID: PMC3279330
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.11.061
Acetylcholinesterase: converting a vulnerable target to a template for antidotes and detection of inhibitor exposure
Abstract
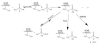
Applications of recombinant DNA technology, chemical synthesis on biological templates and fluorescence detection of organophosphorylation provide unexplored avenues for development of antidotes and approaches for remote detection of organophosphate nerve agents and pesticides. We discuss here how acetylcholinesterase (AChE), through appropriate mutations, becomes more susceptible to oxime reactivation. Since the reaction between organophosphate and the mutated enzyme remains rapid, regeneration of active enzyme by oxime becomes the rate-limiting step in the process to complete a catalytic cycle for generation of active enzyme. Accordingly, "Oxime-assisted Catalysis" by AChE provides a potential means for catalyzing the hydrolysis of organophosphates in plasma prior to their reaching the cellular target site. In turn, AChE, when conjugated with organophosphate, is employed as a template for 'click-chemistry, freeze-frame' synthesis of new nucleophilic reactivating agents that could potentially prove useful in AChE reactivation at the target site as well as in catalytic scavenging of organophosphates in plasma. Finally, substituted AChE molecules can be conjugated to fluorophores giving rise to shifts in emission spectra for detection of dispersed organophosphates. Since external reagents do not have to be added to detect the fluorescence change, the modified enzyme would serve as a remote sensor.
Figures

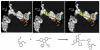

Similar articles
-
SAR study to find optimal cholinesterase reactivator against organophosphorous nerve agents and pesticides.Arch Toxicol. 2016 Dec;90(12):2831-2859. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1827-3. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Arch Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27582056 Review.
-
Rational design, synthesis, and evaluation of uncharged, "smart" bis-oxime antidotes of organophosphate-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 27;295(13):4079-4092. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.012400. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32019865 Free PMC article.
-
Counteracting tabun inhibition by reactivation by pyridinium aldoximes that interact with active center gorge mutants of acetylcholinesterase.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Jun 1;372:40-46. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.04.007. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30978400
-
Limitations in current acetylcholinesterase structure-based design of oxime antidotes for organophosphate poisoning.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016 Aug;1378(1):41-49. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13128. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016. PMID: 27371941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of recombinant DNA methods for production of cholinesterases as organophosphate antidotes and detectors.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2007 Sep;58(3):339-45. doi: 10.2478/v10004-007-0027-1. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2007. PMID: 17913689 Review.
Cited by
-
Utilizing high throughput screening data for predictive toxicology models: protocols and application to MLSCN assays.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2008 Jun-Jul;22(6-7):367-84. doi: 10.1007/s10822-008-9192-9. Epub 2008 Feb 19. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2008. PMID: 18283419
-
Butyrylcholinesterase for protection from organophosphorus poisons: catalytic complexities and hysteretic behavior.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010 Feb 15;494(2):107-20. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2009.12.005. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20004171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of high-affinity phenyltetrahydroisoquinoline aldoximes, linked through anti-triazoles, as reactivators of phosphylated cholinesterases.Toxicol Lett. 2020 Mar 15;321:83-89. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.12.016. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Toxicol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31863869 Free PMC article.
-
From Split to Sibenik: the tortuous pathway in the cholinesterase field.Chem Biol Interact. 2010 Sep 6;187(1-3):3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2010.05.005. Epub 2010 May 20. Chem Biol Interact. 2010. PMID: 20493179 Free PMC article.
-
Phenyl 2-pyridyl ketoxime induces cellular senescence-like alterations via nitric oxide production in human diploid fibroblasts.Aging Cell. 2016 Apr;15(2):245-55. doi: 10.1111/acel.12429. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Aging Cell. 2016. PMID: 26696133 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustinsson KB. Cholinesterases: a study in comparative enzymology. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1948;52:1–182.
-
- Bourne Y, Taylor P, Marchot P. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition by fasciculin: crystal structure of the complex. Cell. 1995;83:493–506. - PubMed
-
- Boyd AE, Marnett AB, Wong L, Taylor P. Probing the active center gorge on acetylcholinesterase by fluorophores linked to substituted cysteines. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:22401–22408. - PubMed
-
- Čalić M, Vrdoljak A. Lucić, Radić B, Jelić D, Jun D, Kuča K, Kovarik Z. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of pyridinium oximes: mode of interaction with acetylcholinesterase, effect on tabun- and soman-poised mice and their cytotoxicity. Toxicology. 2006;219:85–96. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

