Structural investigation of the GlmS ribozyme bound to Its catalytic cofactor
- PMID: 17196404
- PMCID: PMC1847778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.12.005
Structural investigation of the GlmS ribozyme bound to Its catalytic cofactor
Abstract
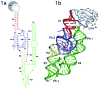
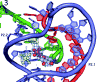
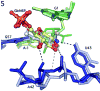
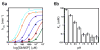
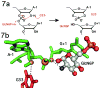
The GlmS riboswitch is located in the 5'-untranslated region of the gene encoding glucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcN6P) synthetase. The GlmS riboswitch is a ribozyme with activity triggered by binding of the metabolite GlcN6P. Presented here is the structure of the GlmS ribozyme (2.5 A resolution) with GlcN6P bound in the active site. The GlmS ribozyme adopts a compact double pseudoknot tertiary structure, with two closely packed helical stacks. Recognition of GlcN6P is achieved through coordination of the phosphate moiety by two hydrated magnesium ions as well as specific nucleobase contacts to the GlcN6P sugar ring. Comparison of this activator bound and the previously published apoenzyme complex supports a model in which GlcN6P does not induce a conformational change in the RNA, as is typical of other riboswitches, but instead functions as a catalytic cofactor for the reaction. This demonstrates that RNA, like protein enzymes, can employ the chemical diversity of small molecules to promote catalytic activity.
Figures

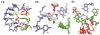
References
-
- Winkler WC, Breaker RR. Regulation of bacterial gene expression by riboswitches. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005;59:487–517. - PubMed
-
- Mandal M, Boese B, Barrick JE, Winkler WC, Breaker RR. Riboswitches control fundamental biochemical pathways in Bacillus subtilis and other bacteria. Cell. 2003;113:577–586. - PubMed
-
- Winkler WC, Nahvi A, Roth A, Collins JA, Breaker RR. Control of gene expression by a natural metabolite-responsive ribozyme. Nature. 2004;428:281–286. - PubMed
-
- Milewski S. Glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase--the multi-facets enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1597:173–192. - PubMed
-
- Hampel KJ, Tinsley MM. Evidence for preorganization of the glmS ribozyme ligand binding pocket. Biochemistry. 2006;45:7861–7871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

