Retinal stem cells transplanted into models of late stages of retinitis pigmentosa preferentially adopt a glial or a retinal ganglion cell fate
- PMID: 17197566
- PMCID: PMC2823590
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.06-0190
Retinal stem cells transplanted into models of late stages of retinitis pigmentosa preferentially adopt a glial or a retinal ganglion cell fate
Abstract
Purpose: To characterize the potential of newborn retinal stem cells (RSCs) isolated from the radial glia population to integrate the retina, this study was conducted to investigate the fate of in vitro expanded RSCs transplanted into retinas devoid of photoreceptors (adult rd1 and old VPP mice and rhodopsin-mutated transgenic mice) or partially degenerated retina (adult VPP mice) retinas.
Methods: Populations of RSCs and progenitor cells were isolated either from DBA2J newborn mice and labeled with the red lipophilic fluorescent dye (PKH26) or from GFP (green fluorescent protein) transgenic mice. After expansion in EGF+FGF2 (epidermal growth factor+fibroblast growth factor), cells were transplanted intravitreally or subretinally into the eyes of adult wild-type, transgenic mice undergoing slow (VPP strain) or rapid (rd1 strain) retinal degeneration.
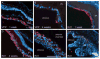
Results: Only limited migration and differentiation of the cells were observed in normal mice injected subretinally or in VPP and rd1 mice injected intravitreally. After subretinal injection in old VPP mice, transplanted cells massively migrated into the ganglion cell layer and, at 1 and 4 weeks after injection, harbored neuronal and glial markers expressed locally, such as beta-tubulin-III, NeuN, Brn3b, or glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), with a marked preference for the glial phenotype. In adult VPP retinas, the grafted cells behaved similarly. Few grafted cells stayed in the degenerating outer nuclear layer (ONL). These cells were, in rare cases, positive for rhodopsin or recoverin, markers specific for photoreceptors and some bipolar cells.
Conclusions: These results show that the grafted cells preferentially integrate into the GCL and IPL and express ganglion cell or glial markers, thus exhibiting migratory and differentiation preferences when injected subretinally. It also appears that the retina, whether partially degenerated or already degenerated, does not provide signals to induce massive differentiation of RSCs into photoreceptors. This observation suggests that a predifferentiation of RSCs into photoreceptors before transplantation may be necessary to obtain graft integration in the ONL.
Figures





References
-
- Rivolta C, Sharon D, DeAngelis MM, Dryja TP. Retinitis pigmentosa and allied diseases: numerous diseases, genes, and inheritance patterns. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:1219–1227. - PubMed
-
- Delyfer MN, Leveillard T, Mohand-Said S, Hicks D, Picaud S, Sahel JA. Inherited retinal degenerations: therapeutic prospects. Biol Cell. 2004;96:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Nishida A, Takahashi M, Tanihara H, et al. Incorporation and differentiation of hippocampus-derived neural stem cells transplanted in injured adult rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:4268–4274. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi M, Palmer TD, Takahashi J, Gage FH. Widespread integration and survival of adult-derived neural progenitor cells in the developing optic retina. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1998;12:340–348. - PubMed
-
- Young MJ, Ray J, Whiteley SJ, Klassen H, Gage FH. Neuronal differentiation and morphological integration of hippocampal progenitor cells transplanted to the retina of immature and mature dystrophic rats. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000;16:197–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

