Mechanism of interactions of alpha-naphthoflavone with cytochrome P450 3A4 explored with an engineered enzyme bearing a fluorescent probe
- PMID: 17198380
- PMCID: PMC2574515
- DOI: 10.1021/bi061944p
Mechanism of interactions of alpha-naphthoflavone with cytochrome P450 3A4 explored with an engineered enzyme bearing a fluorescent probe
Abstract
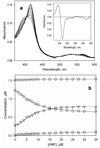
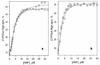
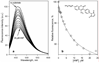
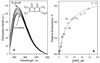
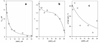
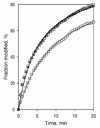
Design of a partially cysteine-depleted C98S/C239S/C377S/C468A cytochrome P450 3A4 mutant designated CYP3A4(C58,C64) allowed site-directed incorporation of thiol-reactive fluorescent probes into alpha-helix A. The site of modification was identified as Cys-64 with the help of CYP3A4(C58) and CYP3A4(C64), each bearing only one accessible cysteine. Changes in the fluorescence of CYP3A4(C58,C64) labeled with 6-(bromoacetyl)-2-(dimethylamino)naphthalene (BADAN), 7-(diethylamino)-3-(4'-maleimidylphenyl)-4-methylcoumarin (CPM), or monobromobimane (mBBr) were used to study the interactions with bromocriptine (BCT), 1-pyrenebutanol (1-PB), testosterone (TST), and alpha-naphthoflavone (ANF). Of these substrates only ANF has a specific effect, causing a considerable decrease in fluorescence intensity of BADAN and CPM and increasing the fluorescence of mBBr. This ANF-binding event in the case of the BADAN-modified enzyme is characterized by an S50 of 18.2 +/- 0.7, compared with the value of 2.2 +/- 0.3 for the ANF-induced spin transition, thus revealing an additional low-affinity binding site. Studies of the effect of TST, 1-PB, and BCT on the interactions of ANF monitored by changes in fluorescence of CYP3A4(C58,C64)-BADAN or by the ANF-induced spin transition revealed no competition by these substrates. Investigation of the kinetics of fluorescence increase upon H2O2-dependent heme depletion suggests that labeled CYP3A4(C58,C64) is represented by two conformers, one of which has the fluorescence of the BADAN and CPM labels completely quenched, presumably by photoinduced electron transfer from the neighboring Trp-72 and/or Tyr-68 residues. The binding of ANF to the newly discovered binding site appears to affect the interactions of the label with the above residue(s), thus modulating the fraction of the fluorescent conformer.
Figures





References
-
- Atkins WM. Non-Michaelis-Menten kinetics in cytochrome P450-catalyzed reactions. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005;45:291–310. - PubMed
-
- Atkins WM. Implications of the allosteric kinetics of cytochrome P450s. Drug Discovery Today. 2004;9:478–484. - PubMed
-
- Yoon MY, Campbell AP, Atkins WM. "Allosterism" in the elementary steps of the cytochrome P450 reaction cycle. Drug Metab. Rev. 2004;36:219–230. - PubMed
-
- Ekins S, Stresser DM, Williams JA. In vitro and pharmacophore insights into CYP3A enzymes. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2003;24:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Khan KK, Liu H, Halpert JR. Homotropic versus heterotopic cooperativity of cytochrome P450eryF: A substrate oxidation and spectral titration study. Drug Metab. Disp. 2003;31:356–359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

