Differences in neonatal mortality among whites and Asian American subgroups: evidence from California
- PMID: 17199070
- PMCID: PMC2376811
- DOI: 10.1001/archpedi.161.1.69
Differences in neonatal mortality among whites and Asian American subgroups: evidence from California
Abstract
Objective: To obtain information about health outcomes in neonates in 9 subgroups of the Asian population in the United States.
Design: Cross-sectional comparison of outcomes for births to mothers of Cambodian, Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Japanese, Korean, Laotian, Thai, and Vietnamese origin and for births to non-Hispanic white mothers. Regression models were used to compare neonatal mortality across groups before and after controlling for various risk factors.
Setting: All California births between January 1,1991, and December 31, 2001.
Participants: More than 2.3 million newborn infants.
Main exposure: Racial and ethnic groups.
Main outcome measure: Neonatal mortality (death within 28 days of birth).
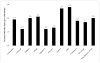
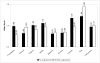
Results: The unadjusted mortality rate for births to non-Hispanic white mothers was 2.0 per 1000. The unadjusted mortality rate for births to Chinese and Japanese mothers was significantly lower (Chinese: 1.2 per 1000, P<.001; Japanese: 1.2 per 1000, P=.004), and for births to Korean mothers the rate was significantly higher (2.7 per 1000, P=.003). For infants of Chinese mothers, observed risk factors explain the differences observed in unadjusted data. For infants of Cambodian, Japanese, Korean, and Thai mothers, differences persist or widen after risk factors are considered. After risk adjustment, infants of Cambodian, Japanese, and Korean mothers have significantly lower neonatal mortality rates compared with infants born to non-Hispanic white mothers (adjusted odds ratios, 0.58 for infants of Cambodian mothers, 0.67 for infants of Japanese mothers, and 0.69 for infants of Korean mothers; all P<.05); infants of Thai mothers have higher neonatal mortality rates (adjusted odds ratio, 1.89; P<.05).
Conclusions: There are significant variations in neonatal mortality between subgroups of the Asian American population that are not entirely explained by differences in observable risk factors. Efforts to improve clinical care that treat Asian Americans as a homogeneous group may miss important opportunities for improving infant health in specific subgroups.
Figures
References
-
- The Diverse Face of Asians and Pacific Islanders in California. Los Angeles, CA: Asian Pacific American Legal Center; 2005.
-
- We the People: Asians in the United States. U.S. Census Bureau; 2004. CENSR-17.
-
- Barnes JS, Bennett CE. The Asian Population: 2000. Washington DC: U.S. Census Bureau; Feb, 2002.

