Alphav beta6 integrin regulates renal fibrosis and inflammation in Alport mouse
- PMID: 17200187
- PMCID: PMC1762706
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060158
Alphav beta6 integrin regulates renal fibrosis and inflammation in Alport mouse
Abstract
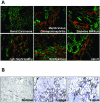
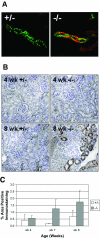
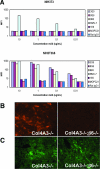
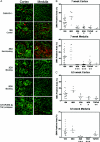
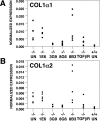
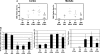
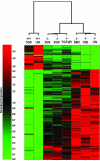
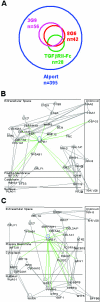
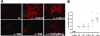
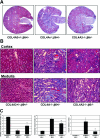
The transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta-inducible integrin alpha v beta6 is preferentially expressed at sites of epithelial remodeling and has been shown to bind and activate latent precursor TGF-beta. Herein, we show that alpha v beta6 is overexpressed in human kidney epithelium in membranous glomerulonephritis, diabetes mellitus, IgA nephropathy, Goodpasture's syndrome, and Alport syndrome renal epithelium. To assess the potential regulatory role of alpha v beta6 in renal disease, we studied the effects of function-blocking alpha v beta6 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and genetic ablation of the beta6 subunit on kidney fibrosis in Col4A3-/- mice, a mouse model of Alport syndrome. Expression of alpha v beta6 in Alport mouse kidneys was observed primarily in cortical tubular epithelial cells and in correlation with the progression of fibrosis. Treatment with alpha v beta6-blocking mAbs inhibited accumulation of activated fibroblasts and deposition of interstitial collagen matrix. Similar inhibition of renal fibrosis was observed in beta6-deficient Alport mice. Transcript profiling of kidney tissues showed that alpha v beta6-blocking mAbs significantly inhibited disease-associated changes in expression of fibrotic and inflammatory mediators. Similar patterns of transcript modulation were produced with recombinant soluble TGF-beta RII treatment, suggesting shared regulatory functions of alpha v beta6 and TGF-beta. These findings demonstrate that alpha v beta6 can contribute to the regulation of renal fibrosis and suggest this integrin as a potential therapeutic target.
Figures
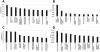
References
-
- Okada H, Kalluri R. Cellular and molecular pathways that lead to progression and regression of renal fibrogenesis. Curr Mol Med. 2005;5:467–474. - PubMed
-
- Sheppard D. Functions of pulmonary epithelial integrins: from development to disease. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:673–686. - PubMed
-
- Norman JT, Fine LG. Progressive renal disease: fibroblasts, extracellular matrix, and integrins. Exp Nephrol. 1999;7:167–177. - PubMed
-
- Border WA, Noble NA. Interactions of transforming growth factor-beta and angiotensin II in renal fibrosis. Hypertension. 1998;31:181–188. - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Koka V, Lan HY. Transforming growth factor-beta and Smad signalling in kidney diseases. Nephrology. 2005;10:48–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

