Complement C1q reduces early atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice
- PMID: 17200212
- PMCID: PMC1762701
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060406
Complement C1q reduces early atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice
Abstract
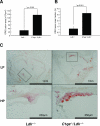
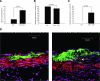
We explored the role of the classic complement pathway in atherogenesis by intercrossing C1q-deficient mice (C1qa-/-) with low-density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice (Ldlr-/-). Mice were fed a normal rodent diet until 22 weeks of age. Aortic root lesions were threefold larger in C1qa-/-/Ldlr-/- mice compared with Ldlr-/- mice (3.72 +/- 1.0% aortic root versus 1.1 +/- 0.4%; mean +/- SEM, P < 0.001). Furthermore, the cellular composition of lesions in C1qa-/-/Ldlr-/- was more complex, with an increase in vascular smooth muscle cells. The greater aortic root lesion size in C1qa-/-/Ldlr-/- mice occurred despite a significant reduction in C5b-9 deposition per lesion unit area, suggesting the critical importance of proximal pathway activity. Apoptotic cells were readily detectable by cleaved caspase-3 staining, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling assay, and electron microscopy in C1qa-/-/Ldlr-/-, whereas apoptotic cells were not detected in Ldlr-/- mice. This is the first direct demonstration of a role for the classic complement pathway in atherogenesis. The greater lesion size in C1qa-/-/Ldlr-/- mice is consistent with the emerging homeostatic role for C1q in the disposal of dying cells. This study suggests the importance of effective apoptotic cell removal for containing the size and complexity of early lesions in atherosclerosis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
No effect of C-reactive protein on early atherosclerosis in LDLR-/- / human C-reactive protein transgenic mice.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Jan;99(1):196-201. doi: 10.1160/TH07-10-0595. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 18217154
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor deficiency impairs atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice.Circulation. 2004 Jun 29;109(25):3149-53. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000134704.84454.D2. Epub 2004 Jun 14. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 15197138
-
Immunoglobulin M is required for protection against atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice.Circulation. 2009 Aug 4;120(5):417-26. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.868158. Epub 2009 Jul 20. Circulation. 2009. PMID: 19620499 Free PMC article.
-
The role of complement in atherosclerosis.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2008 Oct;19(5):478-82. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e32830f4a06. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2008. PMID: 18769228 Review.
-
A proatherogenic role for C-reactive protein in vivo.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005 Oct;16(5):512-7. doi: 10.1097/01.mol.0000180164.70077.a7. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005. PMID: 16148535 Review.
Cited by
-
Autoantibodies against complement component C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Transl Immunology. 2021 Apr 29;10(4):e1279. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1279. eCollection 2021. Clin Transl Immunology. 2021. PMID: 33968409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Complement C1q Activity Is Associated With Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Apr 29;8:618173. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.618173. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33996933 Free PMC article.
-
Platelets and the complement cascade in atherosclerosis.Front Physiol. 2015 Mar 2;6:49. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00049. eCollection 2015. Front Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25784879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clearance of dead cells by efferocytosis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Jul;21(7):398-414. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0232-1. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32251387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of phosphatidylserine recognition receptors in multiple biological functions.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020 Mar 26;25:23. doi: 10.1186/s11658-020-00214-z. eCollection 2020. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32226456 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Walport MJ. Complement. First of two parts. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1058–1066. - PubMed
-
- Walport MJ. Complement. Second of two parts. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1140–1144. - PubMed
-
- Niculescu F, Rus H. Mechanisms of signal transduction activated by sublytic assembly of terminal complement complexes on nucleated cells. Immunol Res. 2001;24:191–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

