Two binding partners cooperate to activate the molecular motor Kinesin-1
- PMID: 17200414
- PMCID: PMC2063617
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200605099
Two binding partners cooperate to activate the molecular motor Kinesin-1
Abstract
The regulation of molecular motors is an important cellular problem, as motility in the absence of cargo results in futile adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis. When not transporting cargo, the microtubule (MT)-based motor Kinesin-1 is kept inactive as a result of a folded conformation that allows autoinhibition of the N-terminal motor by the C-terminal tail. The simplest model of Kinesin-1 activation posits that cargo binding to nonmotor regions relieves autoinhibition. In this study, we show that binding of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase-interacting protein 1 (JIP1) cargo protein is not sufficient to activate Kinesin-1. Because two regions of the Kinesin-1 tail are required for autoinhibition, we searched for a second molecule that contributes to activation of the motor. We identified fasciculation and elongation protein zeta1 (FEZ1) as a binding partner of kinesin heavy chain. We show that binding of JIP1 and FEZ1 to Kinesin-1 is sufficient to activate the motor for MT binding and motility. These results provide the first demonstration of the activation of a MT-based motor by cellular binding partners.
Figures

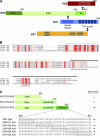
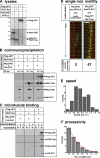
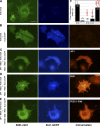
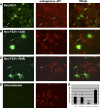
Comment in
-
Jump-starting kinesin.J Cell Biol. 2007 Jan 1;176(1):7-9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200611082. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17200413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adio, S., J. Reth, F. Bathe, and G. Woehlke. 2006. Review: regulation mechanisms of Kinesin-1. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 27:153–160. - PubMed
-
- Coy, D.L., W.O. Hancock, M. Wagenbach, and J. Howard. 1999. Kinesin's tail domain is an inhibitory regulator of the motor domain. Nat. Cell Biol. 1:288–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

