Kinesin-1 structural organization and conformational changes revealed by FRET stoichiometry in live cells
- PMID: 17200416
- PMCID: PMC2063625
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200605097
Kinesin-1 structural organization and conformational changes revealed by FRET stoichiometry in live cells
Abstract
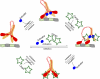
Kinesin motor proteins drive the transport of cellular cargoes along microtubule tracks. How motor protein activity is controlled in cells is unresolved, but it is likely coupled to changes in protein conformation and cargo association. By applying the quantitative method fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) stoichiometry to fluorescent protein (FP)-labeled kinesin heavy chain (KHC) and kinesin light chain (KLC) subunits in live cells, we studied the overall structural organization and conformation of Kinesin-1 in the active and inactive states. Inactive Kinesin-1 molecules are folded and autoinhibited such that the KHC tail blocks the initial interaction of the KHC motor with the microtubule. In addition, in the inactive state, the KHC motor domains are pushed apart by the KLC subunit. Thus, FRET stoichiometry reveals conformational changes of a protein complex in live cells. For Kinesin-1, activation requires a global conformational change that separates the KHC motor and tail domains and a local conformational change that moves the KHC motor domains closer together.
Figures
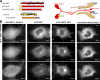
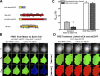
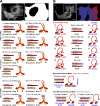


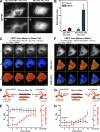

Comment in
-
Jump-starting kinesin.J Cell Biol. 2007 Jan 1;176(1):7-9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200611082. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17200413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adio, S., J. Reth, F. Bathe, and G. Woehlke. 2006. Review: regulation mechanisms of Kinesin-1. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 27:153–160. - PubMed
-
- Coy, D.L., W.O. Hancock, M. Wagenbach, and J. Howard. 1999. Kinesin's tail domain is an inhibitory regulator of the motor domain. Nat. Cell Biol. 1:288–292. - PubMed

