The pancreatic stellate cell: a star on the rise in pancreatic diseases
- PMID: 17200706
- PMCID: PMC1716214
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI30082
The pancreatic stellate cell: a star on the rise in pancreatic diseases
Abstract
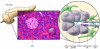
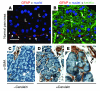
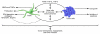
Pancreatic stellate cells (PaSCs) are myofibroblast-like cells found in the areas of the pancreas that have exocrine function. PaSCs are regulated by autocrine and paracrine stimuli and share many features with their hepatic counterparts, studies of which have helped further our understanding of PaSC biology. Activation of PaSCs induces them to proliferate, to migrate to sites of tissue damage, to contract and possibly phagocytose, and to synthesize ECM components to promote tissue repair. Sustained activation of PaSCs has an increasingly appreciated role in the fibrosis that is associated with chronic pancreatitis and with pancreatic cancer. Therefore, understanding the biology of PaSCs offers potential therapeutic targets for the treatment and prevention of these diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Watari N., Hotta Y., Mabuchi Y. Morphological studies on a vitamin A-storing cell and its complex with macrophage observed in mouse pancreatic tissues following excess vitamin A administration. Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn. 1982;58:837–858. - PubMed
-
- Ikejiri N. The vitamin A-storing cells in the human and rat pancreas. Kurume Med. J. 1990;37:67–81. - PubMed
-
- Bachem M.G., et al. Identification, culture, and characterization of pancreatic stellate cells in rats and humans. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:421–432. - PubMed
-
- Whitcomb D.C. Inflammation and cancer. V. Chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004;287:G315–G319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- DK47918/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK047918/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AA015781/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK073909/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK052951/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AA15781/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA11999/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DK56339/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK52951/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK73909/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056339/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA011999/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052951/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

