Liver heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins independently of LDL receptor family members
- PMID: 17200715
- PMCID: PMC1716206
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI29154
Liver heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins independently of LDL receptor family members
Abstract
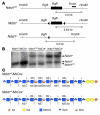
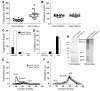
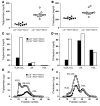
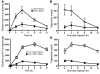
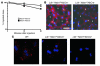
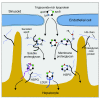
We examined the role of hepatic heparan sulfate in triglyceride-rich lipoprotein metabolism by inactivating the biosynthetic gene GlcNAc N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 (Ndst1) in hepatocytes using the Cre-loxP system, which resulted in an approximately 50% reduction in sulfation of liver heparan sulfate. Mice were viable and healthy, but they accumulated triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particles containing apoB-100, apoB-48, apoE, and apoCI-IV. Compounding the mutation with LDL receptor deficiency caused enhanced accumulation of both cholesterol- and triglyceride-rich particles compared with mice lacking only LDL receptors, suggesting that heparan sulfate participates in the clearance of cholesterol-rich lipoproteins as well. Mutant mice synthesized VLDL normally but showed reduced plasma clearance of human VLDL and a corresponding reduction in hepatic VLDL uptake. Retinyl ester excursion studies revealed that clearance of intestinally derived lipoproteins also depended on hepatocyte heparan sulfate. These findings show that under normal physiological conditions, hepatic heparan sulfate proteoglycans play a crucial role in the clearance of both intestinally derived and hepatic lipoprotein particles.
Figures
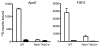
Comment in
-
Atherogenic remnant lipoproteins: role for proteoglycans in trapping, transferring, and internalizing.J Clin Invest. 2007 Jan;117(1):94-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI30889. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17200713 Free PMC article.
-
Liver heparan sulfate proteoglycans: old molecules provide new insights on lipoprotein metabolism.Hepatology. 2007 Apr;45(4):1078-80. doi: 10.1002/hep.21647. Hepatology. 2007. PMID: 17393511 No abstract available.
References
-
- Conrad, H.E. 1998. Heparin-binding proteins. Academic Press. San Diego, California, USA. 527 pp.
-
- Bernfield M., et al. Functions of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999;68:729–777. - PubMed
-
- Esko J.D., Selleck S.B. Order out of chaos: assembly of ligand binding sites in heparan sulfate. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002;71:435–471. - PubMed
-
- Williams K.J., Fuki I.V. Cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans: dynamic molecules mediating ligand catabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1997;8:253–262. - PubMed
-
- Belting M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycan as a plasma membrane carrier. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003;28:145–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

