HER-2 and NF-kappaB as the targets for therapy-resistant breast cancer
- PMID: 17201139
- PMCID: PMC3658609
HER-2 and NF-kappaB as the targets for therapy-resistant breast cancer
Abstract
HER-2 (also called ErbB2 or Neu) tyrosine kinase, one of the four members of ErbB receptor family (ErbB1, i.e., EGFR ErbB2, ErbB3 and ErbB4), plays a critical role in the control of diverse cellular functions involved in differentiation, proliferation, migration and cell survival via multiple signal transduction pathways. Overexpression of HER-2, observed in HER-2-positive breast cancer patients, is believed to cause the tumor resistance to an array of anti-cancer agents and poor prognosis. Although HER-2 antibodies have shown growth inhibitory effects, more efficient molecular targets against HER-2-mediated tumor resistance need to be developed. The molecular mechanisms underlying HER-2-mediated tumor resistance, especially the connections between HER-2 and therapy-resistant signaling networks, need to be further investigated. NF-kappaB, a key stress transcription factor that can initiate a pro-survival network, was found to be activated in many cancer cells overexpressing HER-2 and to be responsible for the radiation resistance in HER-2 transfected breast cancer cells. Recent findings in literature and data from this laboratory suggest a possible co-operation between HER-2 and NF-KB in signaling tumor resistance to radiotherapy. This review will discuss the mechanisms of HER-2 mediated NF-kappaB signaling pathway and potential target for therapeutic intervention.
Figures
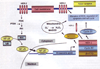
References
-
- Schechter AL, Stern DF, Vaidyanathan L, Decker SJ, Drebin JA, Greene MI, Weinberg RA. The neu oncogene: an erb-B-related gene encoding a 185,000-Mr tumour antigen. Nature. 1984;312:513–516. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama T, Sudo C, Ogawara H, Toyoshima K, Yamamoto T. The product of the human c-erbB-2 gene: a 185-kilodalton glycoprotein with tyrosine kinase activity. Science. 1986;232:1644–1646. - PubMed
-
- Way TD, Lin JK. Role of HER2/HER3 co-receptor in breast carcinogenesis. Fut Oncol. 2005;1:841–849. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
