Radiosensitization by 2-benzoyl-3-phenyl-6,7-dichloroquinoxaline 1,4-dioxide under oxia and hypoxia in human colon cancer cells
- PMID: 17201910
- PMCID: PMC1770925
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-2-1
Radiosensitization by 2-benzoyl-3-phenyl-6,7-dichloroquinoxaline 1,4-dioxide under oxia and hypoxia in human colon cancer cells
Abstract
Background: The sensitizing effects of 2-benzoyl-3-phenyl-6,7-dichloroquinoxaline 1,4-dioxide (DCQ) and ionizing radiation (IR) were determined in four colon cancer cells and in FHs74Int normal intestinal cells.
Methods: Cell cycle modulation, TUNEL assay, clonogenic survival and DNA damage were examined under oxia or hypoxia. Effects on apoptotic molecules and on p-Akt and Cox-2 protein expression were investigated.
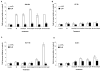
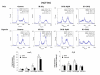
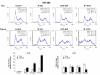
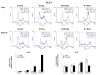
Results: The four cell lines responded differently to DCQ+IR; HT-29 cells were most resistant. Combination treatment caused significant increases in preG1 (apoptosis) in HCT-116, while G2/M arrest occurred in DLD-1. DCQ potentiated IR effects more so under hypoxia than oxia. Pre-exposure of DLD-1 to hypoxia induced 30% apoptosis, and G2/M arrest in oxia. The survival rate was 50% lower in DCQ+IR than DCQ alone and this rate further decreased under hypoxia. FHs74Int normal intestinal cells were more resistant to DCQ+IR than cancer cells.Greater ssDNA damage occurred in DLD-1 exposed to DCQ+IR under hypoxia than oxia. In oxia, p-Akt protein expression increased upon IR exposure and drug pre-treatment inhibited this increase. In contrast, in hypoxia, exposure to IR reduced p-Akt protein and DCQ restored its expression to the untreated control. Apoptosis induced in hypoxic DLD-1 cells was independent of p53-p21 modulation but was associated with an increase in Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and the inhibition of the Cox-2 protein.
Conclusion: DCQ is a hypoxic cell radiosensitizer in DLD-1 human colon cancer cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Radiosensitization of EMT6 mammary carcinoma cells by 2-benzoyl-3-phenyl-6,7-dichloroquinoxaline 1,4-dioxide.Radiother Oncol. 2008 Mar;86(3):412-8. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2007.10.013. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Radiother Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18006096
-
The radiosensitizer 2-benzoyl-3-phenyl-6,7-dichloroquinoxaline 1,4-dioxide induces DNA damage in EMT-6 mammary carcinoma cells.Radiat Oncol. 2009 Jul 14;4:25. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-4-25. Radiat Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19594955 Free PMC article.
-
Cell death by the quinoxaline dioxide DCQ in human colon cancer cells is enhanced under hypoxia and is independent of p53 and p21.Radiat Oncol. 2010 Nov 15;5:107. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-5-107. Radiat Oncol. 2010. PMID: 21078189 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis by 2-benzoyl-3-phenyl-6,7-dichloroquinoxaline 1,4-dioxide in adult T-cell leukemia cells.Chem Biol Interact. 2004 Jul 20;148(3):101-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2004.05.002. Chem Biol Interact. 2004. Retraction in: Chem Biol Interact. 2018 Jan 5;279:243. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.11.015. PMID: 15276867 Retracted.
-
Flavonoids sensitize tumor cells to radiation: molecular mechanisms and relevance to cancer radiotherapy.Int J Radiat Biol. 2020 Mar;96(3):360-369. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1694193. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Int J Radiat Biol. 2020. PMID: 31738629 Review.
Cited by
-
The quinoxaline di-N-oxide DCQ blocks breast cancer metastasis in vitro and in vivo by targeting the hypoxia inducible factor-1 pathway.Mol Cancer. 2014 Jan 24;13:12. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-12. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24461075 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis induction and tumor cell repopulation: the yin and yang of radiotherapy.Radiat Oncol. 2011 Dec 19;6:176. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-176. Radiat Oncol. 2011. PMID: 22182804 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
PIDA-mediated intramolecular oxidative C-N bond formation for the direct synthesis of quinoxalines from enaminones.RSC Adv. 2019 Mar 7;9(14):7718-7722. doi: 10.1039/c9ra01200a. eCollection 2019 Mar 6. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35521175 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer, anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of aminoalcohol-based quinoxaline small molecules.Acta Cir Bras. 2024 Aug 5;39:e395124. doi: 10.1590/acb395124. eCollection 2024. Acta Cir Bras. 2024. PMID: 39109780 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of Erufosine in nude mice--implications for combination with radiotherapy.Radiat Oncol. 2009 Oct 23;4:46. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-4-46. Radiat Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19852786 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

